You use PCR to genotype Juliet, her child, Alex, and Hugo at the polymorphic locus PS6 . The PS6 locus is shown below as a gray box, along with 10 base pairs of flanking sequence on each side of the PS6 locus. Which set of primers shown below would you use to amplify the PS6 locus? Circle one primer set. (5 pts)
![]()
Primer set 1:
|
Primer set 2:
|
Primer set 3:
|
Primer set 4:
|
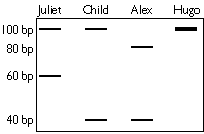 You use gel electrophoresis to separate the DNA products
obtained from each of the PCR reactions. The gel is depicted on the right.
You use gel electrophoresis to separate the DNA products
obtained from each of the PCR reactions. The gel is depicted on the right.
PS6 is a microsatellite repeat locus with repeat units of two (2) base pairs in length. Using this information, and not taking the length of the primers into consideration , determine the genotype (repeat numbers) of each person at PS6. (12 pts)
Juliet: ____________ Alex ____________
Child ____________ Hugo ____________
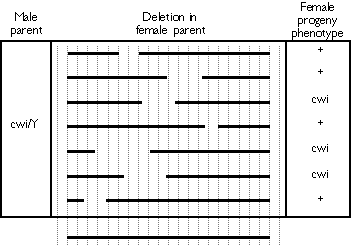
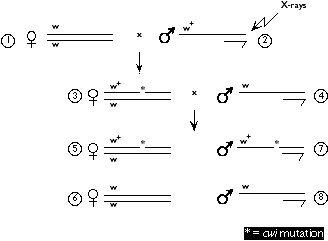 (14 pts total) H.J. Muller's
experiment to estimate the mutation frequency in Drosophila yielded a variety
of strains of flies that carry recessive lethal mutations. In addition,
his crosses yielded some strains that carry mutations that do NOT cause
lethality when recessive but do cause other phenotypes. You are interested
in the process of wing formation, so you identify a strain of Muller's that
carries a non-lethal X-chromosome mutation that causes crumpled wings. The
crosses shown depict Muller's cross that generated the crumpled wings (cwi
) mutation. [NOTE: w+ and w are the same white gene alleles that you heard
about in lecture.]
(14 pts total) H.J. Muller's
experiment to estimate the mutation frequency in Drosophila yielded a variety
of strains of flies that carry recessive lethal mutations. In addition,
his crosses yielded some strains that carry mutations that do NOT cause
lethality when recessive but do cause other phenotypes. You are interested
in the process of wing formation, so you identify a strain of Muller's that
carries a non-lethal X-chromosome mutation that causes crumpled wings. The
crosses shown depict Muller's cross that generated the crumpled wings (cwi
) mutation. [NOTE: w+ and w are the same white gene alleles that you heard
about in lecture.]