
Scenario 2
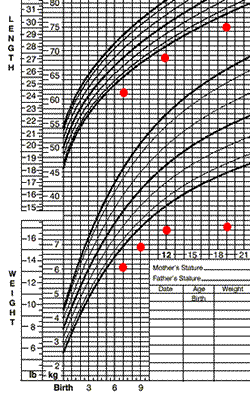
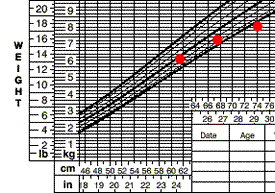
Frank is a 19-month old with developmental delay, but no significant oral-motor problems. His rate of weight gain has slowed over the past few months.
You are asked to evaluate his nutritional status and make recommendations to improve his weight gain.
Frank’s mother describes his food pattern.
He is taking about 15-18 ounces of infant formula that is concentrated to 30 kilocalories per ounce each day and eating some solid foods. Mom says that mealtime is a “battle” and that the family usually has to force Frank to eat.
His family adds foods like heavy cream to the solid foods he is offered, to increase the energy density.
Mom says that Frank has recently started to refuse to open his mouth very wide, making it difficult for him to take large volumes. A week or so ago, he began refusing all solid foods, but his intake is slowly increasing again.
Frank’s mother says that he has been seen by a feeding therapist, who was working on increasing his intake of solid foods. The family felt that Frank was not making much progress, so discontinued the therapy.
You calculate Frank’s estimated energy intake and review his medical record.
 |
 |
||
|
|||