Home
Neuroprotective actions of estrogen |
||
 |
 |
|
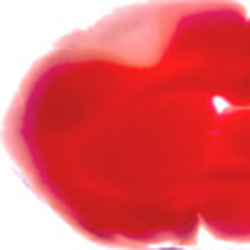
During the past decade, we have begun to appreciate important trophic as well as protective roles of estrogen in adult and aging brains. Numerous studies that utilize a variety of animal models show that estrogen prevents cell death, promotes neuronal survival, enhances neurite outgrowth, stimulates synaptogenesis and regulates synthesis of neurotransmitters and their receptors under a wide range of experimental paradigms. Previously, we have shown that low physiological levels of 17beta-estradiol exert profound neuroprotective actions in a model of stroke-injury in which the middle cerebral artery is permanently occluded. Estrogen achieves these actions by altering the expression of multiple genes involved in cell death/survival pathways, leading to increased neuronal survival in the penumbra that surrounds the ischemic core. Brain sections shown here are stained using 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride, which stains live tissues as bright red. |
||
References: