participants
Birth Defects of the Limb
This study aims to find genes that cause birth defects of the limb such as clubfoot, missing fingers, etc. The specific conditions studied are listed below. Click on each condition to learn more.
- Distal Arthrogryposis (DA)
- Holt Oram Syndrome (HOS)
- Ulnar Mammary Syndrome (UMS)
- Split-Hand-Foot Malformation Syndrome (SHFM)
- Ectrodactyly-Ectodermal Dysplasia-Cleft Palate (EEC)
Distal Arthrogryposis
 Arthrogryposis is simply a term used to describe an individual with congenital contractures or a limitation of movement, of two or more different body areas (e.g., ankle, elbow, knee). The distal arthrogryposis (DA) disorders primarily affect the distal joints of the limbs such as the joints of the hands and feet. There are several types of DA that are classified based on other clinical problems that are associated with the limb malformations. You can click on the links below to find out more about the different types of DA.
Arthrogryposis is simply a term used to describe an individual with congenital contractures or a limitation of movement, of two or more different body areas (e.g., ankle, elbow, knee). The distal arthrogryposis (DA) disorders primarily affect the distal joints of the limbs such as the joints of the hands and feet. There are several types of DA that are classified based on other clinical problems that are associated with the limb malformations. You can click on the links below to find out more about the different types of DA.
Distal Arthrogryposis Type 1 (DA1)
Distal Arthrogryposis Type 1 (DA1) is characterized by contractures of the hands, clubfoot, and dislocated hips. These characteristics are common to all of the DA Syndromes. Each of the other DA Syndromes are characterized by additional features. DA1 is caused by mutations in a gene called TPM2 that encodes tropomyosin 2.
Freeman Sheldon Syndrome (FSS or DA2A)
 Freeman Sheldon Syndrome (FSS) is characterized by contractures of the hands, clubfoot as well as contractures of the facial muscles. The contracted facial muscles result in a tight, pinched mouth, "H-shaped" dimpling of the chin, deep creases around the mouth and downward slanting eyes. Individuals with FSS can also have crossed eyes or problems aligning the eyes simultaneously (strabismus). This form of DA is also known as "whistling face syndrome" because of the striking facial features. FSS is caused by mutations in a gene called MYH3 that encodes a myosin protein.
Freeman Sheldon Syndrome (FSS) is characterized by contractures of the hands, clubfoot as well as contractures of the facial muscles. The contracted facial muscles result in a tight, pinched mouth, "H-shaped" dimpling of the chin, deep creases around the mouth and downward slanting eyes. Individuals with FSS can also have crossed eyes or problems aligning the eyes simultaneously (strabismus). This form of DA is also known as "whistling face syndrome" because of the striking facial features. FSS is caused by mutations in a gene called MYH3 that encodes a myosin protein.
Sheldon Hall Syndrome (SHS or DA2B)
Sheldon Hall Syndrome (SHS) is a recently defined form of distal arthrogryposis that is often confused with FSS. Individuals with SHS have contractures of the hands, clubfoot, vertical talus, deep creases around the mouth, downward slanting eyes and a small mouth. Sheldon-Hall is the most common of the DA syndromes and can be caused by mutations in at least three different genes: TNNI2, TNNT3, and MYH3.
- Myosin Heavy Chain 3 (MYH3) is located on chromosome 17p13.3. Mutations in MYH3 were found in ~32% of the individuals with SHS.
- Troponin I (TNNI2) is located on chromosome 11p15.5. Mutations in TNNI2 are found in less than 10% of the cases of SHS.
- Troponin T (TNNT3) is located on chromosome 11p15.5. TNNT3 also accounts for less than 10% of the mutations found in individuals with SHS in our studies.
Genes Involved in SHS
Distal Arthrogryposis Type 5 (DA5)
Distal Arthogryposis Type 5 is characterized by contractures of the hands, feet and the muscles that control the movements of the eye. People with DA5 frequently also have weak or sagging eyelids (ptosis).
Trismus Pseudo-Camptodactyly (TPC or DA7)
Trismus Pseudo-Camptodactyly (TPC) is characterized by contractures of the muscles that control opening of the mouth. This limits the ability to open the mouth completely (trismus). In addition, the fingers of affected individuals can't be straightened completely when the wrist is flexed upward. This is called pseudo-camptodactyly.
TPC is caused by a mutation in a gene called MYH8 that encodes a myosin protein.
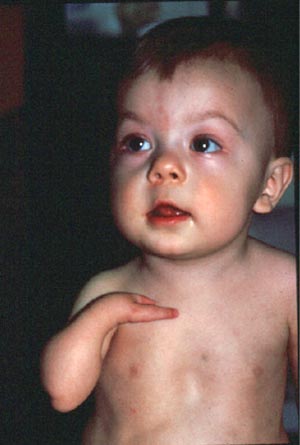
Holt Oram Syndrome (HOS)
 Holt Oram Syndrome (HOS) is a disorder characterized by birth defects of the radial side of the upper limbs (the side of the arm with the thumb) and defects of the heart.
Holt Oram Syndrome (HOS) is a disorder characterized by birth defects of the radial side of the upper limbs (the side of the arm with the thumb) and defects of the heart.
The most common heart defects observed in patients with HOS are atrial septal defects (ASD) and ventricular septal defects (VSD). Limb defects observed in HOS range from absence of most of a limb to an extra bone in the thumb. Other limb defects include under-development of a limb, hand, or thumb and fusion of the bones of the wrist. Both sides of the body are usually affected, but each side can be affected differently.
HOS is caused by mutations in a gene called TBX5.
Ulnar Mammary Syndrome (UMS)
Ulnar Mammary syndrome (UMS) is a disorder characterized by birth defects of the ulnar side of the upper limbs (the side of the arm with the pinky finger) and the breasts. Teeth, kidneys, and the sweat glands in the armpits are also sometimes affected. UMS is caused by mutations in a gene called TBX3.
Split-Hand-Foot Malformation Syndrome (SHFM)
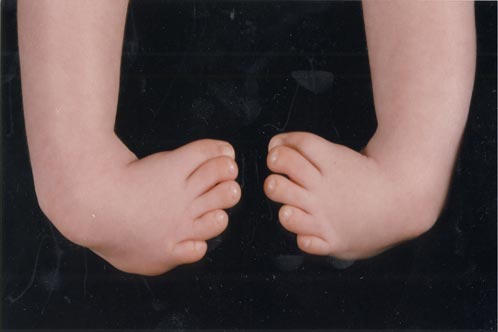
 Split-Hand-Foot Malformation Syndrome (SHFM) is a disorder characterized by abnormalities of the bones of the hands and feet. Typically, the bones of the middle digits are most severely affected resulting in a hand or a foot that looks as though it has been split down the middle. SHFM is often referred to as ectrodactyly. SHFM can be an isolated finding - meaning that only the limbs are affected - or it can be associated with abnormalities of other body parts. Many cases of isolated SHFM are caused by an abnormality of chromosome 10.
Split-Hand-Foot Malformation Syndrome (SHFM) is a disorder characterized by abnormalities of the bones of the hands and feet. Typically, the bones of the middle digits are most severely affected resulting in a hand or a foot that looks as though it has been split down the middle. SHFM is often referred to as ectrodactyly. SHFM can be an isolated finding - meaning that only the limbs are affected - or it can be associated with abnormalities of other body parts. Many cases of isolated SHFM are caused by an abnormality of chromosome 10.
Ectrodactyly-Ectodermal Dysplasia-Cleft Palate (EEC)
Ectrodactyly-Ectodermal Dysplasia (ECC) is a form of SHFM in which other body parts are also affected. In this case, the other body parts are the skin, hair, nails, and teeth (structures derived from the ectoderm or outer layer of cells of a developing baby). Affected individuals frequently have cleft lip and palate. EEC is caused by mutations in a gene called TP63.