| 5. |
Fleet-footedness in the Puyallup Pig is controlled genetically
(pigs can be fast or slow), as is Oreo-craving (pigs can love
or hate Oreo cookies). The two traits segregate independently.
Two crosses are performed. In Cross 1, true-breeding slow Oreo-lovers
are mated with true-breeding slow Oreo-haters. In Cross 2, true-breeding
fast Oreo-lovers are mated with true-breeding slow Oreo-haters.
The progeny from Cross 1 are mated with the progeny from Cross
2. The resulting progeny are as follows:
| Phenotype |
Number of progeny |
| fast Oreo-hater |
61 |
| slow Oreo-hater |
58 |
| slow Oreo-lover |
22 |
| fast Oreo-lover |
19 |
Explain these crosses (genotypes and phenotypes, dominant vs.
recessive), using F and f to describe dominant and recessive with respect to speed, and
L and l for dominant and recessive with respect to Oreo-loving. |
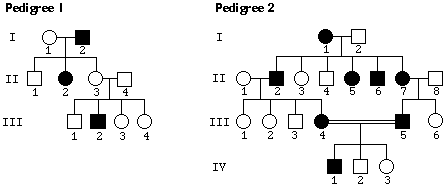
 After talking to a patient who has come in for counseling, a genetic
counselor draws up a pedigree for the patient's family. Which
of the modes of inheritance listed in question 3(b) can explain
this pedigree? (For each mode that you eliminate, briefly explain
why you did so.) Suggest three independent explanations for this pedigree.
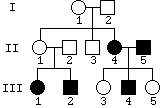
After talking to a patient who has come in for counseling, a genetic
counselor draws up a pedigree for the patient's family. Which
of the modes of inheritance listed in question 3(b) can explain
this pedigree? (For each mode that you eliminate, briefly explain
why you did so.) Suggest three independent explanations for this pedigree.