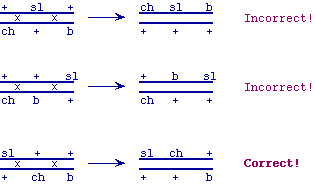
(18 pts total)
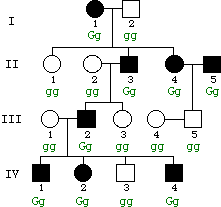
Below is a pedigree that shows the inheritance of green hair in a human family (individuals with green hair are shown as affected ). Assume complete expressivity and penetrance.

Which one of the following modes of inheritance best fits this pedigree? (Circle one.) (8 pts)
- (i) autosomal recessive (not consistent -- affected couple II-4 and II-5 have unaffected
child)
- (ii) autosomal dominant <-- this is the best fit (all others are not consistent)!
- (iii) X-linked recessive (not consistent -- affected woman II-4 has unaffected father I-2)
- (iv) X-linked dominant (not consistent -- affected man II-3 has unaffected daughter III-3)
- (ii) autosomal dominant <-- this is the best fit (all others are not consistent)!
Based on your answer in (a), write the genotypes of all individuals in the pedigree in the space beneath each individual. Use G for the dominant allele and g for recessive. (4 pts)
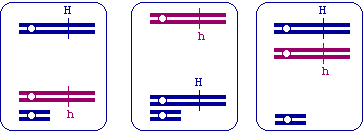
A second trait, purple eyes, is determined by a second gene, and segregates perfectly with the green hair trait. In other words, all individuals in the pedigree with green hair also have purple eyes, while individuals without green hair do not have purple eyes. What can you say about the positions of the loci for these two traits? (ONE sentence!) (2 pts)
| Since the traits segregate together, the two loci must be linked. |
Individuals III-1 and III-2 had another child after this pedigree was drawn. This youngest child (not included above) has green hair, but DOES NOT have purple eyes. Given your answer in part (b), what event could explain this outcome, and which person was involved? (4 pts)
| Recombination between the two loci must have occurred in the heterozygous parent (III-2). |
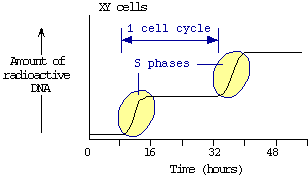 A tissue culture cell line was established from a normal (XY)
male. Tissue culture cells that were just about to enter mitosis
were incubated with radioactively labeled DNA precursors. Cell
samples were withdrawn at regular intervals, and the amount of
radioactive DNA in each sample was plotted:
A tissue culture cell line was established from a normal (XY)
male. Tissue culture cells that were just about to enter mitosis
were incubated with radioactively labeled DNA precursors. Cell
samples were withdrawn at regular intervals, and the amount of
radioactive DNA in each sample was plotted: