|

 |
Advanced materials
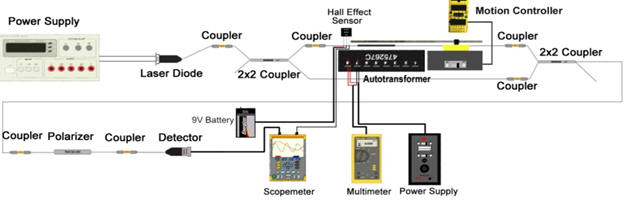
1. Polymer based fiber-optic magnetostrictive metal detector. The dector utilizes fiber-optic Mach-Zehnder interferometer with a newly developed ferromagnetic polymer as the metal sensing material. This metal detector system is much less complex, relatively smaller in size, and easy to fabricate. Additionally the technique is free from RF interference.
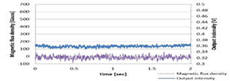
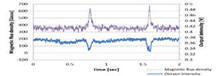
2. Tunable Terahertz fishnet metamaterial. In contrast to other PDLC-based devices, the TFMM employs a novel method for encapsulating PDLC using a thin (1.5 lm) polyimide “skin layer” to form a uniform surface for metal electrodes while minimizing the Fabry-Perot effect of the skin layer on the TFMM measurements. The tunability was verified by measuring the frequency shift in the reflection coefficient (0.01 THz), with an observed minimum negative refractive index of 15 at 0.55 THz.
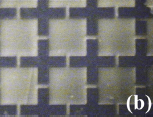 PDLC-TFMM testing sample: microscopic view of PLDC-TFMM at 0V |
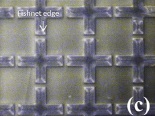 PDLC-TFMM testing sample: microscopic view of PLDC-TFMM at 280 V |
3. Conductive polymer. The conductive polymer has a large amount of advantages such as significantly reduced weight, ease of manufacturing, ease of integration directly to existing structures, compatibility with existing micro-nano fabrication technology, printability, and variety of host polymer materials available.
 |
 |