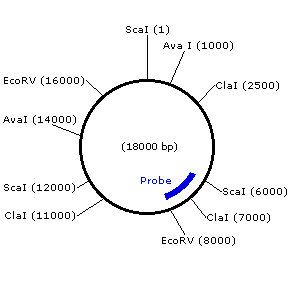
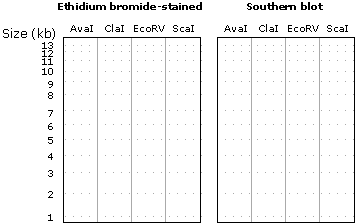
In the outline of the gel (left panel), draw the bands you would expect to see for each digest. (Ethidium bromide is a dye that fluoresces when bound to DNA. By soaking a gel with ethidium bromide and then taking a picture of the gel in UV light, one can detect all the DNA bands in the gel. See page 49 of your lecture notes for an example.)
In the panel on the right ("Southern blot") draw the bands you would expect to see if the gel was hybridized in a Southern blot experiment to the "Probe" fragment indicated in the DNA map. (The DNA sequence of the "Probe" fragment is identical to that of coordinates 6000 - 8000 of the circular DNA shown in the map.)