|
I. IntroductionThe RiboTag procedure allows simple and efficient isolation of ribosome-associated mRNAs from specific cell types in complex tissues, including brain. The RiboTag approach takes advantage of the stability of the complexes that are formed when mRNA is productively assembled with the ribosome during translation of proteins; these mRNA-ribosome complexes are stable to freezing and the snap frozen tissue can be stored at 80°C for later analysis. The RiboTag mouse has a modified Ribosomal Protein L22 (RPL22), which is one of the 79 core proteins that constitute the ribosome particle as it is assembled in the nucleolus. The final coding exon 4 of the Rpl22 gene is flanked by LoxP recombination sites followed by an identical final exon 4 that has three hemagglutinin (HA) epitope coding sequences inserted before the final STOP codon of the gene. When the RiboTag mouse is crossed to a Cre Driver mouse, the Cre recombinase enzyme is activated in the cell type of interest, resulting in removal of the LoxP-flanked wild type Rpl22 exon 4 and replacement with the HA-tagged Rpl22 exon 4. Following excision of the wild type Rpl22 exon 4, RPL22-HA protein is expressed and incorporated into the ribosome particle.
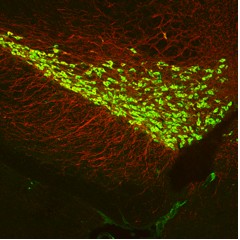
Figure 1. RiboTag mouse expressing RPL22-HA tagged ribosomes in dopaminergic neurons of the VTA and SNc. A Dopamine Transporter-Cre Driver mouse was crossed to a RiboTag mouse to obtain DAT-Cre+:RiboTag+ offspring. HA in green and TH in red. |
The RiboTag mouse offers the following benefits:1) Endogenous expression: RPL22-HA is expressed under the endogenous promoters and thus in concert with the other core ribosomal proteins. 2) Single breeding step: A homozygotic RiboTag mouse can be crossed directly to any existing Cre Driver line (typically bred as heterozygotes) yielding 50% of offspring that can be used for the RiboTag immunoprecipitation procedure. This greatly reduces both animal housing time and the number of animals needed. 3) Versatile: RiboTag is compatible with any Cre Driver line as well as techniques that employ viral Cre recombinase injections. |
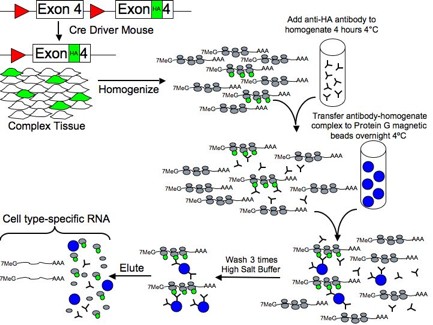
II. RiboTag Procedure Figure 2. The RiboTag MethodFor the RiboTag procedure, female homozygous RiboTag mice (available from Jackson Laboratories) can be crossed to a male cell type-specific or inducible Cre Driver mouse to obtain experimental offspring that are Cre-Driver+:RiboTag+. Whole brain or micro-dissected/micro-punched brain tissue can be used in the RiboTag IP procedure. The procedure requires approximately 2 days from the point of making the brain homogenate to having cell type-specific RNA ready for analysis by microarray, RNAseq, or qRT-PCR. Multiple Cre Driver+:RiboTag+ experiments can be run in parallel and whole brain or micro-dissected tissue can also be snap frozen for later RiboTag IP analysis. Link to Updated and Simplified Protocol RiboTag IP Procedure (2014) |
Brief Overview of the ProcedureDay One1) The mouse is sacrificed and the brain tissue is quickly removed and placed in a pre-chilled Dounce homogenizer with sufficient homogenization buffer (50mM Tris, pH 7.4, 100mM KCl, 12mM MgCl2, 1mM DTT, 1% Nonidet P40, 200 units/ml Promega purified RNasin, 100ug/ml cycloheximide, 1mg/ml heparin, and Sigma Protease Inhibitor Cocktail) to create a 3% weight/volume homogenate. Alternatively, tissue can be flash-frozen and stored long-term at 80°C. 2) After Douncing on ice to create the homogenate, the sample is centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 10min to create a post-mitochondrial supernatant and the homogenate transferred to a cold tube on ice. 3) 800ul of the homogenate is transferred to a microfuge tube and 2-5ul of Covance HA.11 ascites antibody (2mg/ml) is added to the homogenate, which is then rotated in the cold room for 4 hours. 4) After 4 hours, 400ul of Invitrogen Dynal Protein G magnetic beads in a new tube are washed and aspirated dry. The antibody-homogenate sample (800ul) is transferred to the beads and rotated overnight in the cold room. Day Two5) The following morning, the microfuge tube is placed in a magnetic rack causing the magnetic beads to move to the side of the tube and the supernatant is removed. 6) High salt wash buffer (50mM Tris, pH 7.4, 300mM KCl, 12mM MgCl2, 0.5mM DTT, 1% Nonidet P40, 200 units/ml Promega purified RNasin, 100ug/ml cycloheximide, 1mg/ml heparin, and Sigma Protease Inhibitor Cocktail) is then added to the magnetic beads that now contain the ribosome-associated cell-type-specific mRNAs and rotated in the cold room for 5min. 7) The washes are repeated a total of three times, the final wash supernatant is removed, and 600ul of RLT reagent + Beta-mercaptoethanol from the Qiagen RNeasy mini prep kit is added to the beads. The sample can be stored at -80°C or processed immediately to purify total RNA. 8) Purify RNA using Qiagen RNeasy mini or micro plus kit, as appropriate. Store or analyze purified RNA as desired. |
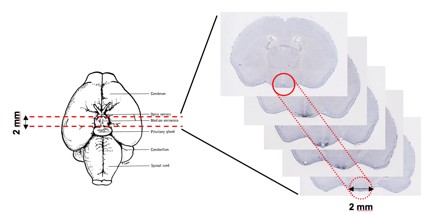
III. RNA extraction from a small brain regionFor micro-dissections or micro-punches used to isolate specific brain regions such as the hypothalamus, mice are sacrificed and the brain removed to a Harvard brain matrix. Sterile razor blades are placed to demarcate the hypothalamus and a coronal section containing the hypothalamus is laid onto a sterile cold metal block. The hypothalamus is isolated using a Harris Uni-Core 2.0mm punch and transferred to a sterile cold glass Dounce homogenizer containing 1mL of the homogenization buffer. Two to four mice are used depending on the abundance of the cell population. After homogenizing the 1-2mm punches of the hypothalamus, the homogenate is centrifuged to create the post-mitochondrial supernatant and the RiboTag immunoprecipitation reaction performed exactly as it is for the whole brain. Total RNA in this case is prepped using the Qiagen RNeasy Micro Plus kit.
Figure 3. Microdissection of hypothalamus (in situ images from Allen Brain Institute)For the RiboTag procedure, female homozygous RiboTag mice (available from Jackson Laboratories) can be crossed to a male cell type-specific or inducible Cre Driver mouse to obtain experimental offspring that are Cre-Driver+:RiboTag+. Whole brain or micro-dissected/micro-punched brain tissue can be used in the RiboTag IP procedure. The procedure requires approximately 2 days from the point of making the brain homogenate to having cell type-specific RNA ready for analysis by microarray, RNAseq, or qRT-PCR. Multiple Cre Driver+:RiboTag+ experiments can be run in parallel and whole brain or micro-dissected tissue can also be snap frozen for later RiboTag IP analysis. |
IV. RNA analysisWe generally start by verifying sample quality by quantitative real-time PCR for mRNAs known to be specifically expressed in the target neurons and use beta-actin mRNA as a control. We also use an oligodendrocyte marker mRNA, such as 2', 3'-Cyclic-nucleotide 3' phosphodiesterase (CNP) or transferrin, that is not expressed in neurons to assess background. Samples are then analyzed further by microarray or qRT-PCR, depending on the aims of the experiment. Typical results:1) 20-200 fold enrichments for the target mRNA in the IP and a de-enrichment for the oligodendrocyte and glial mRNAs. 2) 30% overall yield of a specific mRNA from the total lysate. |