| Mycorrhizae | ||
| Jess Michalak + Virginia Werner Winter 2012 |
||
| Introduction | ||
|
||
|
||
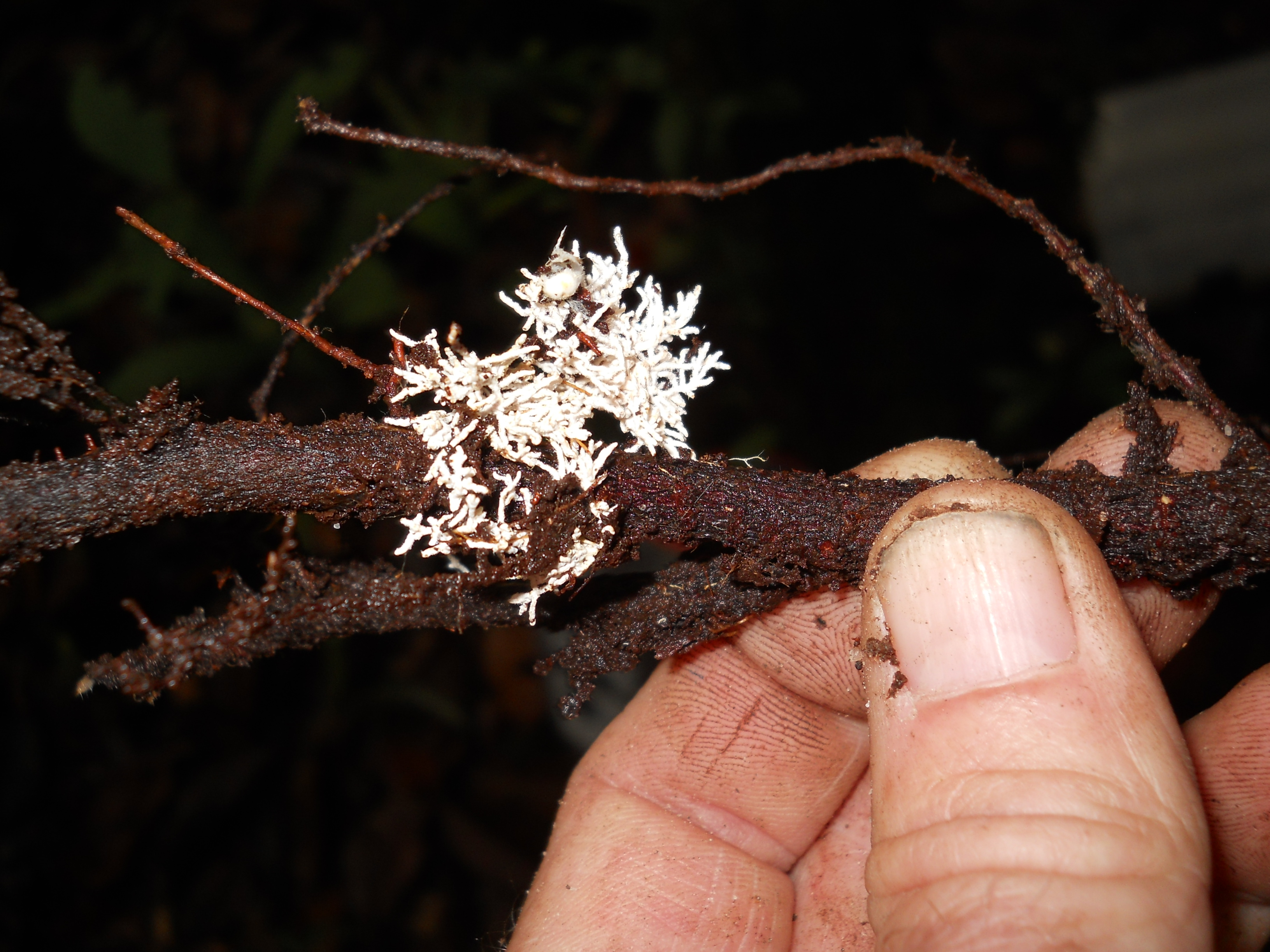
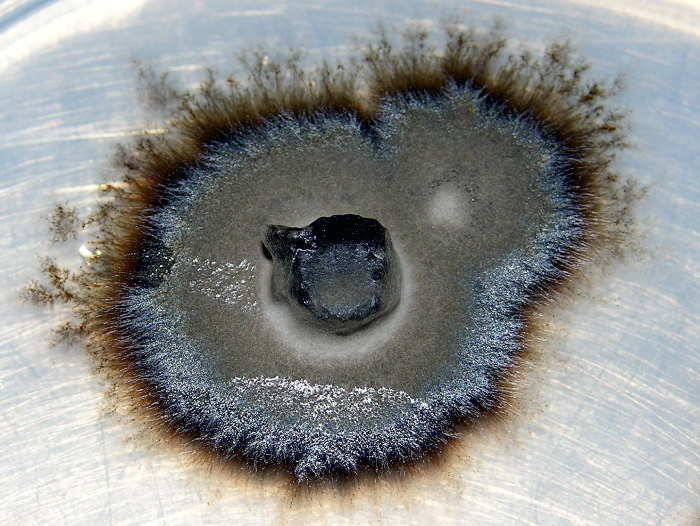
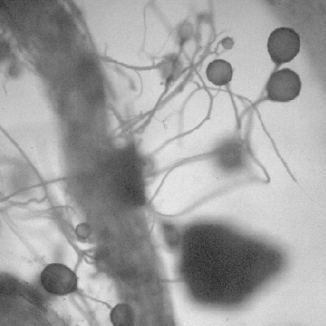
Mycorrhizae are fungi that typically have a symbiotic relationship with the root systems of plants. The symbiotic exchange has the potential to increase plants’ growth considerably. It involves the transfer of glucose from the plant’s roots to for the additional nutrients and water the fungi produce. There are a variety of methods of inoculation which are discussed in detail later. This section explores the benefits, costs, and considerations of Mycorrhizal inoculation. Mycorrhizal inoculation has been used successfully in the disturbed roadside conditions of the interstate highway system since the 1980’s, and is commonly used in agriculture as well. This topic is of specific relevance to landscape architects as it has also been successfully used to restore badly damaged and sterile landscapes. Mycorrhizal inoculation classes are becoming part of the continuing education system, Landscape Architecture Continuing Education System* or LA CES, and are being taught by at least one company. *LA CES is a collaborative system created by the American Society of Landscape Architects (ASLA), Canadian Society of Landscape Architects (CSLA), Council of Educators in Landscape Architecture (CELA), Council of Landscape Architectural Registration Boards (CLARB), Landscape Architectural Accreditation Board (LAAB), and Landscape Architecture Foundation (LAF).
|
||
|
||