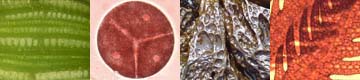
Color: Dark red to black when dessicated. Brilliant red color is attributed to the relatively large amounts of phycoerythrin in comparison to phycocyanin in the phycobilisomes.
Size: Thalli approximately 10-35 cm tall (Abbott 1976).
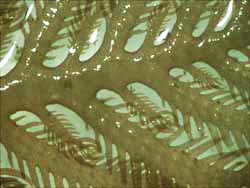
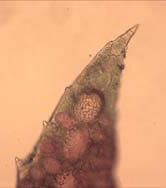
Micro Morphology: Uniaxial with several pronounced axial branches of indeterminate growth each possessing opposite lateral branchlets that are markedly different in size, one of determinate and the other of indeterminate growth. Each branchlet bears leaflets with acute tips and serrate margins.
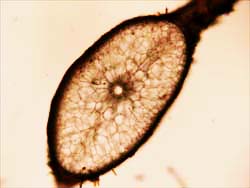
The thallus is corticated, except at the apices of the branches, and several layers thick. The cortex develops early and is composed of a few layers of smaller cells as well as larger storage oriented cells.
Individual cells are uninucleate with pit plugs present between cells, a characteristic of the Class Florideophyceae. Chloroplasts are mostly ribbon shaped.
Macro Morphology: saxicolous (grows on rocks) but can be epiphytic. Attaches to substrate via multicellular filaments arising from the basal cells of the lower branches.
Abbott, Isabella A. and George J. Hollenberg. Marine Algae of California. Stanford University Press. Stanford CA. 1976.
Fritsch, F.E. The Structure and Reproduction of the Algae. Cambridge University Press. London, UK. 1945. |