Lariat: Visual Analytics for Exploring Social Media Data
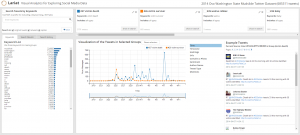 Lariat is a social media research tool for exploring Twitter data. The design stemmed from a series of interviews with social scientists and a participatory design process. One key feature of Lariat that helps social scientists make sense of their data is the ability to generate plots on the fly and use them to drill down into a specific subset of Tweets.
Lariat is a social media research tool for exploring Twitter data. The design stemmed from a series of interviews with social scientists and a participatory design process. One key feature of Lariat that helps social scientists make sense of their data is the ability to generate plots on the fly and use them to drill down into a specific subset of Tweets.
The tool has not been officially released yet, but the current prototype can be found on GitHub.
Agave: Collaborative Exploration of Twitter Data
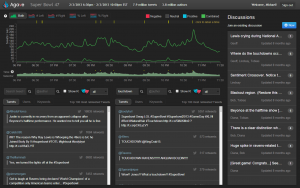 Agave is a web application for collaboratively exploring millions of tweets. You can visit Agave to see how it works on Twitter data that we have collected. Agave’s main features are an interactive timeline showing changes in tweet rate and sentiment over time, searching and filtering, and built-in annotation and discussion with others (requires Twitter sign-in).
Agave is a web application for collaboratively exploring millions of tweets. You can visit Agave to see how it works on Twitter data that we have collected. Agave’s main features are an interactive timeline showing changes in tweet rate and sentiment over time, searching and filtering, and built-in annotation and discussion with others (requires Twitter sign-in).
Agave is useful for finding the broad characteristics of a new data set, such as key events and topics being discussed. Initial exploratory analysis can help provide a more grounded direction for future analysis. Support for multiple users enables all members of a research team to participate in this phase of the project and to share their findings from within the tool. Agave works great on data gathered using the Twitter Streaming API over a period of hours or days, but longer time spans can also work.
Agave development is on GitHub. You are welcome to download, run, and modify your own version with your own data. Questions and problems can be posted on the GitHub issue tracker.
ALOE: Affect Labeler of Expressions
We developed ALOE to train and test machine learning classifiers for automatically labeling chat messages with different emotion or affect categories. The software takes as input a CSV file containing timestamped chat messages with labels for training and produces a trained Support Vector Machine classifier as described in our CSCW 2013 paper, Statistical Affect Detection in Collaborative Chat.
Once a classifier has been trained, ALOE can use the classifier to label other unlabeled message data. It also features an interactive mode, where chat messages can be entered one at a time for classification.
ALOE is open source software issued under the GNU General Public License.
Hoptrees: visual hierarchy navigation
Hoptrees are a visual navigation interface developed by HDS Lab in collaboration with researchers from Eigenfactor.org. Hoptrees make it easier for people to keep track of where they are and where they’ve been when navigating hierarchical information. For example, they could help you avoid getting lost in your file system, or on a complex hierarchical website. A paper about hoptrees, Hoptrees: Branching History Navigation for Hierarchies, was published at INTERACT 2013.
We have created an open source prototype hoptree implementation in JavaScript issued under both the BSD license and the GNU General Public License.
- Read more about our research on hoptrees
- See a hoptree in action
- Check out our open-source prototype on GitHub
Text Prizm: qualitative analysis of large social media data
To support our research on emotion in collaborative work, we are developing Text Prizm, a web application to help you analyze social media content (such as chat logs or Twitter data). Text Prizm will provide the following features:
- Simultaneous open coding by a team of researchers over large text data sets.
- Minimally painful coding – a lightweight coding interface driven by easy keyboard shortcuts.
- Exposure to all coded data in a portable, open format.
- Collaborative iteration on a structured coding scheme through memo-writing and visualizations.
- Develop custom analyses based on human-in-the-loop active learning to extend coding over the entire data set
- Interactive visualizations that provide access to the underlying text, preserve context, and support qualitative research methods.
If you are interested in hearing from us when Text Prizm is available, join this mailing list!