What is Joubert Syndrome?
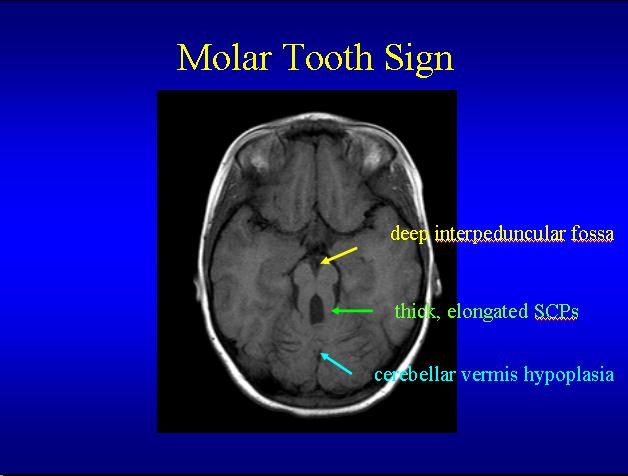
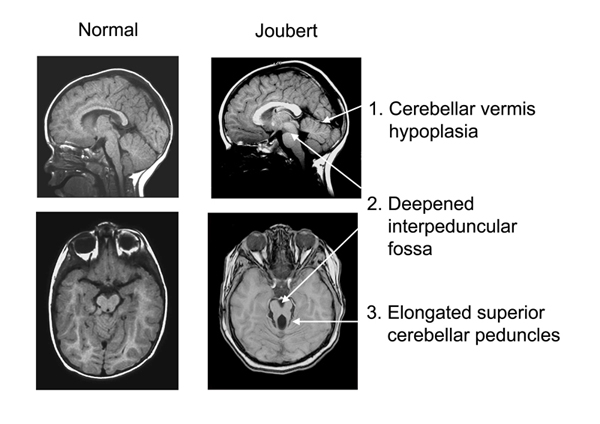
Joubert syndrome is a neurogenetic disorder characterized by hypotonia, developmental disability, abnormal breathing pattern, abnormal eye movements, and a distinctive brain malformation giving the appearance of "the molar tooth sign" on axial brain MRI. In addition to developmental disability and the brain malformation, subsets of patients have coloboma (a gap in the retina of the eye), polydactyly (extra fingers or toes), and other malformations, and some patients also develop retinal dystrophy, cystic kidney disease, and/or liver fibrosis. The neurologic symptoms (hypotonia, impaired coordination, abnormal eye movements, poor speech articulation, and abnormal breathing pattern) reflect the parts of the brain most affected in patients with Joubert: the cerebellar vermis and brainstem. Joubert syndrome is inherited in a recessive manner, so once a couple has had a child with Joubert syndrome, they have a 25% chance of having another affected child each time they get pregnant. Identifying the genes responsible for Joubert syndrome has helped define a new category of diseases called the "ciliopathies" because all of the Joubert syndrome genes seem to be involved with an important cellular structure called the primary cilium. The primary cilium acts as an antenna for most cells in the body, allowing the cells to detect the environment outside the cell and react to it.
Health Care Recommendations
For health care recommendations, please see the Joubert Syndrome & Related Disorders website.