|
Classification of Cells or Batteries
Electrochemical batteries
are classified into 4 broad categories.
A primary cell or
battery is one that cannot easily be
recharged after one use, and are discarded following discharge.
Most primary cells utilize electrolytes that are contained within
absorbent material or a
separator
(i.e. no free or liquid electrolyte), and are thus termed dry cells.
A secondary cell
or battery is one that can be electrically recharged after use to their
original pre-discharge condition, by passing current through the circuit
in the opposite direction to the current during discharge. The following
graphic evidences the recharging process.
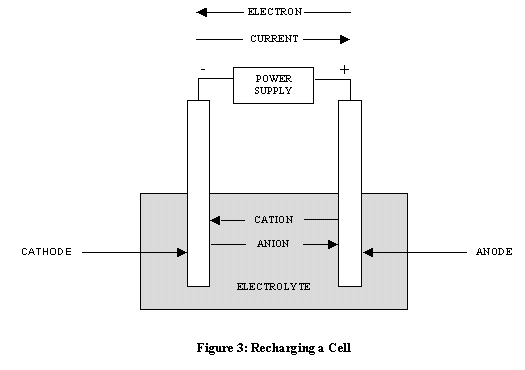
Secondary batteries fall
into two sub-categories depending on their intended applications.
-
Cells that are utilized
as energy storage devices, delivering energy on demand. Such cells are
typically connected to primary power sources so as to be fully charged
on demand. Examples of these type of secondary cells include emergency
no-fail and standby power sources, aircraft systems and stationary
energy storage systems for
load-leveling.
Primary
vs. Secondary – A Comparison
The following table
summarizes the pros and cons of primary and secondary
batteries.
Primary
|
Secondary
|
|
Lower initial cost.
Higher life-cycle cost ($/kWh).
Disposable.
Disposable.
Replacement readily available.
Typically lighter and smaller;
thus traditionally more suited for portable applications.
Longer service per charge and
good
charge retention.
Not ideally suited for heavy load/high
discharge rate performance.
Not ideally suited for
load-leveling, emergency backup,
hybrid battery, and high cost
military applications.
Traditionally limited to specific
applications.
|
Higher initial cost.
Lower
life-cycle cost ($/kWh) if charging in convenient and inexpensive.
Regular maintenance required.
Periodic recharging required.
Replacements while available, are
not produced in the same sheer numbers as primary batteries. May need
to be pre-ordered.
Traditionally less suited for
portable applications, although recent advances in Lithium battery
technology have lead to the development of smaller/lighter secondary
batteries.
Relative to primary battery systems,
traditional secondary batteries (particularly aqueous secondary
batteries) exhibit inferior charge retention.
Superior
high discharge rate performance at heavy loads
Ideally suited for
load-leveling, emergency backup, hybrid battery and high cost military
applications
The overall inherent
versatility of secondary battery systems allows its use and continuing
research for a large spectrum of applications.
|
A third battery category is
commonly referred to as the reserve cell. What differentiates the
reserve cell from primary and secondary cells in the fact that a key
component of the cell is separated from the remaining components, until
just prior to activation. The component most often isolated is the
electrolyte. This battery structure is commonly observed in thermal
batteries, whereby the electrolyte remains inactive in a solid state until
the melting point of the electrolyte is reached, allowing for ionic
conduction, thus activating the battery. Reserve batteries effectively
eliminate the possibility of self-discharge and minimize chemical
deterioration. Most reserve batteries are used only once and then
discarded. Reserve batteries are used in timing, temperature and pressure
sensitive detonation devices in missiles, torpedoes, and other weapon
systems.
Reserve cells are typically
classified into the following 4 categories.
-
Water activated
batteries.
-
Electrolyte activated
batteries.
-
Gas activated batteries.
-
Heat activated
batteries.
The
fuel cell represents the fourth category of batteries. Fuel
cells are similar to batteries except for the fact that that all active
materials are not an integral part of the device (as in a battery).
In fuel cells, active materials are fed into batteries from an outside
source. The fuel cell differs from a battery in that it possesses
the capability to produce electrical energy as long as active materials
are fed to the electrodes, but stop operating in the absence of such
materials. A well-known application of fuel cells has been in cryogenic
fuels used in space vehicles. Use of fuel cell technology for terrestrial
applications has been slow to develop, although recent advances have
generated a revitalized interest in a variety of systems with applications
such as utility power, load-leveling, on-site generators and electric
vehicles.
Home |
Previous | Next |
