|
|
| M A T E R I A L S C I E N C E & E N G I N E E R I N G |
|||||||
|
|
|
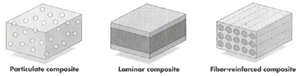
Material Classes Composites A composite material is made up of a matrix and a reinforcement phase. Composites take advantage of directional properties of the reinforcement phase and gluing properties of the matrix. The reinforcement phase may be any material in fiber, platelet, or aggregate form.
The matrix phase must be able to flow around the reinforcement and later hardened. Metals, ceramics, and polymers are all regularly used for man-made composites. Polymer composites are lightweight non-metallic material systems made up of high strength fibers embedded in plastic matrix material. Polymer composites are what you think of when you think of composite materials.
Most composites are difficult to manufacture due to the complex processing needed. New techniques in composite processing have made it easier to make sporting equipment, space shuttle parts, and car parts out of composites.
|
||||
| Copyright © 2006 CES Information Guide - Materials Science Engineering |
|||||||