The Effect of Antisolvent Treatment on the Growth of 2D/3D Tin Perovskite Films for Solar Cells
Abstract
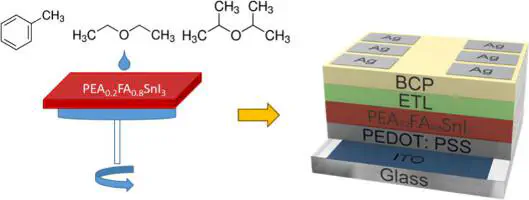
Antisolvent treatment is used in the fabrication of perovskite films to control grain growth during spin coating. We study widely incorporated aromatic hydrocarbons and aprotic ethers, discussing the origin of their performance differences in 2D/3D Sn perovskite (PEA0.2FA0.8SnI3) solar cells. Among the antisolvents that we screen, diisopropyl ether yields the highest power conversion efficiency in solar cells. We use a combination of optical and structural characterization techniques to reveal that this improved performance originates from a higher concentration of 2D phase, distributed evenly throughout the 2D/3D Sn perovskite film, leading to better crystallinity. This redistribution of the 2D phase, as a result of diisopropyl ether antisolvent treatment, has the combined effect of decreasing the Sn4+ defect density and background hole density, leading to devices with improved open-circuit voltage, short-circuit current, and power conversion efficiency.