| Heart Sounds & Murmurs | | | [Liver & Ascites] | | | Neck Veins | | | Pulmonary | | | Thyroid |
|
[Skill Modules
>>
Liver & Ascites
]
Introduction: Examination of Liver and Ascites
Several maneuvers for examining the liver and for detecting ascites are described in this module.
Technique: Liver size
Technique: Ascites
Associated FindingsRelated history and physical examination findings are described. An important aspect of ascites is the analysis of ascitic fluid and determination of the serum - ascites albumin gradient, helpful in differential diagnosis. Evidence BaseSeveral studies have evaluated how the accuracy of the physical examination in assessing liver size and detecting ascites. The evidence based section can guide the examiner in making a clinical determination of abnormal liver size and whether or not ascites is present |
||||||||||||||||
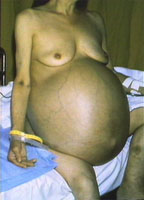 The right upper quadrant of the abdomen can be examined to look for changes in the size or consistency of the liver. Additionally, examination of the abdomen can reliably indicate (fluid in the peritoneal cavity ) is present. Ascites is a common sequelae of liver disease. Patients with obesity can be distinguished from those with ascites by careful examination.
The right upper quadrant of the abdomen can be examined to look for changes in the size or consistency of the liver. Additionally, examination of the abdomen can reliably indicate (fluid in the peritoneal cavity ) is present. Ascites is a common sequelae of liver disease. Patients with obesity can be distinguished from those with ascites by careful examination.