
phase transitions and the pluripotent state
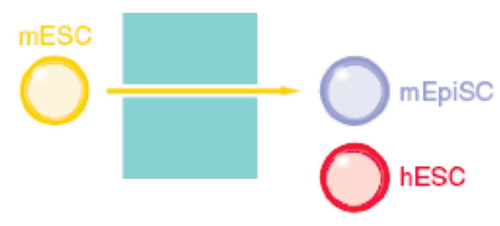
Mouse embryonic stem cells (ESC) are derived from the pre-implantation embryo. In 2007, two groups described a new type of mouse stem cell derived from the post-implantation embryo, called the epiblast stem cell (EpiSC) (Tesar et al., Nature 2007). Although EpiSC can form most tissues, they differ from ESC in their morphological appearance, culture requirements, and gene expression profile. Interestingly, human ESC are similar in their appearance and culture requirements to EpiSC.
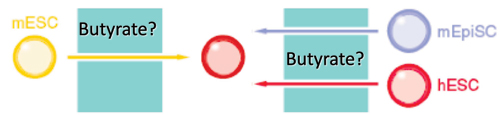
Our collaborator, Carol Ware, discovered that a low, narrow concentration of the histone deacetylase Inhibitor, sodium butyrate, can support the self renewal of ESC from humans, mice, and non-human primates (Ware et al., Cell Stem Cell 2009). Butyrate appears to induce a change in stem cell state. Gene expression profiling suggests that human ESC pulled backward to an earlier developmental stage, whereas mouse ESC are pushed forward.
Papers
Ware CB, Chien S, and Blau CA. Slow, Controlled-Rate Freezing Improves Human Embryonic Stem Cell Survival. Biotechniques 38:879-883, 2005.
Ware CB, Nelson, AM, and Blau CA. A Comparison of NIH-Approved Human Embryonic Stem Cell Lines. Stem Cells 24:2677-84, 2006.
Wang L, Schulz TC, Sherrer ES, Dauphin DS, Shin S, Nelson AM, Ware CB, Zhan M, Song C-Z, Chen X, Brimble SN, Amanda M, Galeano MJ, Uhl EW, Damour KA, Chesnut J, Rao MS, Blau CA and Robins AJ. Self-renewal of human embryonic stem cells requires insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and ERBB2 receptor signaling. Blood 110:4111-9, 2007.
Ware CB, Wang L, Mecham BH, Nelson AM, Dauphin DS, Buckingham B, Bar M, Lim R, Askari B, Gartler SM, Shen L, Issa J-P, Tewari M, Lamba DA, Pavlidis P, Duan Z, and Blau CA. Histone Deacetylase Inhibition Elicits an Evolutionarily Conserved Self-Renewal Program in Embryonic Stem Cells. Cell Stem Cell 4:359-369, 2009.