|
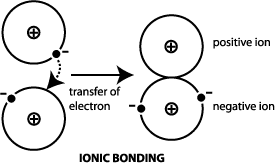
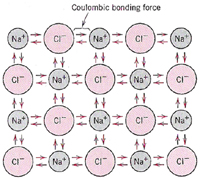
Definition: A metallic bond
is formed when the valence electrons are not associated with
a particular atom or ion, but exist as a "cloud" of
electrons around the ion centers.
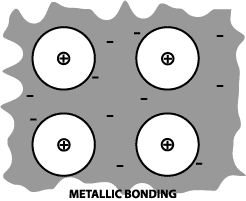
Metallic materials have good electrical
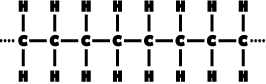
and thermal conductivity when compared to materials with covalent
or ionic bonding. A metal such as iron has metallic bonding. |
Example: In
the real and imperfect world, most materials do not have pure
metallic, pure covalent, or pure ionic bonding; they may
have other types of bonding as well. For example, iron has predominantly
metallic bonding, but some covalent bonding also occurs.

This wrench, found in a car shop in Malaysia,
has been subjected to much abuse and is clearly showing signs
of age. In its current condition, signs of rust shows that,
at a molecular level, its metallic bonding is not perfect and
the bending indicates that the original crystalline
structure is altered. |