[Skill Modules
>>
Heart Sounds & Murmurs
>>
Techniques
]
Techniques: Heart Sounds & Murmurs
Clicks and Snaps
Clicks
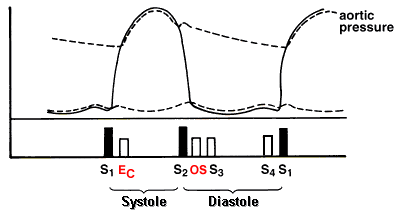
EC=ejection click :: OS=opening snap
Ejection click
Most common early systolic sound; Results from abrupt halting of semilunar valves
Aortic ejection click:
Description:
Loud high frequency sound, associated with murmur due to same etiology
Does not vary with respiration
Location:
Best heard at apex
Clinical significance:
Causes associated with aortic valve with decreased but some residual mobility:
i.e., aortic stenosis, bicuspid aortic valves and dilated aortic root; not generally
heard with calcific aortic stenosis due to non-mobile valve
Pulmonic ejection click:
Description:
Early systolic ejection sound with associated murmur. Often diminishes with
inspiration.
Location:
Sternal edge 2nd or 3rd ICS
Clinical significance:
Causes associated with pulmonic valve: pulmonic stenosis, pulmonary hypertension
and dilated pulmonary trunk
back to top
Opening snap
Description:
High-frequency early diastolic sound (occurs 50-100 msec after A2) associated
with mitral stenosis; sound due to abrupt deceleration of mitral leaflets sound
with associated murmur. Often diminishes with inspiration' accentuated in left
lateral position.
Location:
Between apex and left lower sternal border
Sounds like:
RUP bu Dup rrrrrrRup Bu Dup
Correlating to s1, s2, OS, murmur of mitral stenosis,
Clinical significance:
The OS plus typical murmur indicates the murmur is due to mitral stenosis and
not a flow rumble across a non-stenotic valve. The timing of the OS has been
suggested as a gauge of the severity of the stenosis but has not been found
to be reliable for this.
Mid-systolic click (plus late systolic murmur of mitral valve prolapse)
back to top
Others:
Prosthetic valves
Prosthetic mitral valve sounds:
- opening sound analogous to opening snap
- closing sound coincides with S1
Prosthetic aortic valve sounds:
- opening sound analogous to ejection click
- closing sound coincides with S2
Proceed to the next technique
|
