[Skill Modules
>>
Neck & Veins Examination
>>
Evidence Base
]
Evidence Base - Neck Veins
Cardiac Hemodynamics
The following tables and graph depict the correlation of bedside-measured jugular venous pressure (JVP) with cardiac catheterization hemodynamics in patient with chronic congestive heart failure. The pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP) is considered elevated if >18 mm Hg, and is a sign of fluid overload. Elevated JVP is referred to as jugular venous distention (JVD).
Jugular Venous Distention and Pulmonary Capillary Wedge Pressure
| |
PCWP <18 mm Hg |
PCWP >18 mm Hg |
| JVD absent |
14* |
1* |
| JVD present |
16* |
21* |
| |
* Number of patients |
back to top
Jugular Venous Distention, Hepatojugular Reflux (HJR), and Pulmonary Capillary Wedge Pressure
back to top
PCWP in Relation to Clinical Findings of JVD and HJR
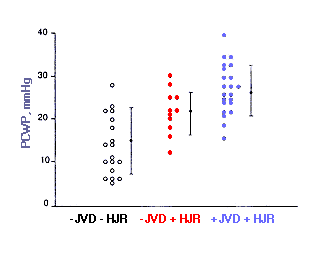 |
- Patients without JVD and with negative HJR
- Patients without JVD but with positive HJR
- Patients with both JVD and positive HJR
|
Adapted from Butman, et al
|
