[Skill Modules
>>
Neck & Veins Examination
>>
Laboratory & Imaging
]
Laboratory & Imaging: Neck Veins
The etiology of heart failure is divided into three categories: elevated left ventricular (LV) filling pressure, LV ejection fraction under 40%, and diastolic dysfunction.
Ancillary tests enhance the ability to diagnose which type of heart failure is present. Below is a summary of echocardiography and radiology data, and findings most suggestive in each category of heart failure.
| Postero-anterior view |
Lateral View |
click for full size |

click for full size |
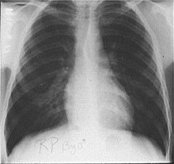
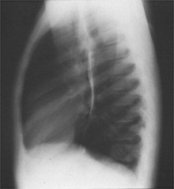
| Normal chest x-ray with normal pulmonary veins |
 |
 |
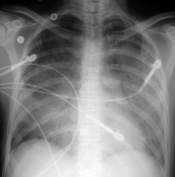
| Chest x-ray with pulmonary edema |
 |
back to top
Data from one study comparing the sensitivity and specificity of jugular venous distention with other studies are shown:
| Clinical Findings to Detect Types of Heart Failure |
Sensitivity Range |
Specificity Range |
| Increased filling pressure |
| Radiographic redistribution |
10% to 58% |
79% to 100% |
|
| Jugular venous distention |
55% to 65% |
74% to 80% |
| Ejection fraction <40% |
| Radiographic cardiomegaly or redistribution |
4% to 33% |
87% to 100% |
| Anterior q-waves |
32% to 44% |
89% |
| Left-bundle branch block |
18% |
95% |
| Abnormal apical impulse |
31% to 36% |
89% to 95% |
| Diastolic dysfunction |
| Current hypertension |
60% to 61% |
59% to 70% |
|




