VIRUS-HOST INTERACTIONS
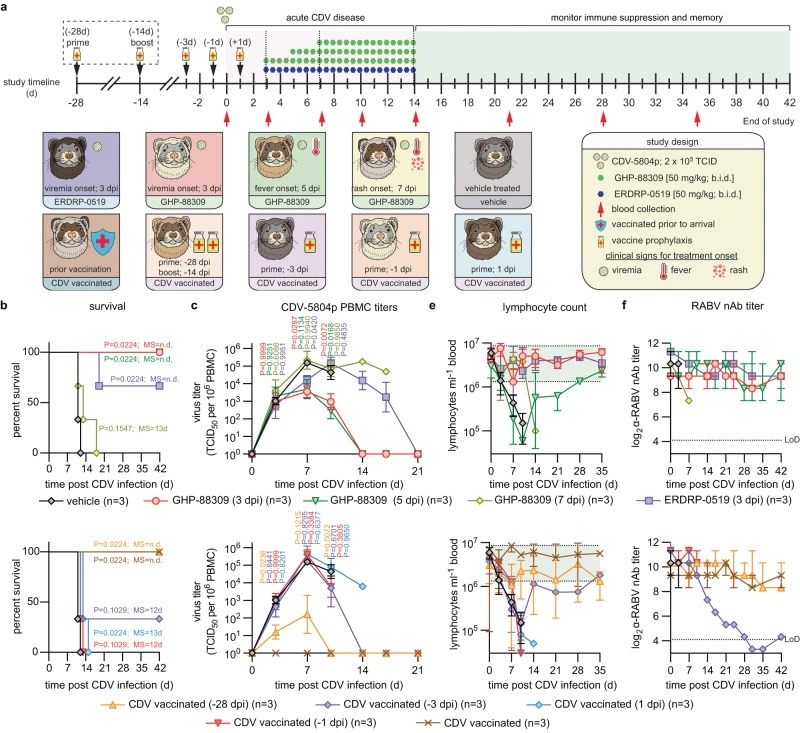
Therapeutic mitigation of measles-like immune amnesia and exacerbated disease after prior respiratory virus infections in ferrets
Measles cases have surged pre-COVID-19 and the pandemic has aggravated the problem. Most measles-associated morbidity and mortality arises from destruction of pre-existing immune memory by measles virus (MeV), a paramyxovirus of the morbillivirus genus. Therapeutic measles vaccination lacks efficacy, but little is known about preserving immune memory through antivirals and the effect of respiratory disease history on measles severity.
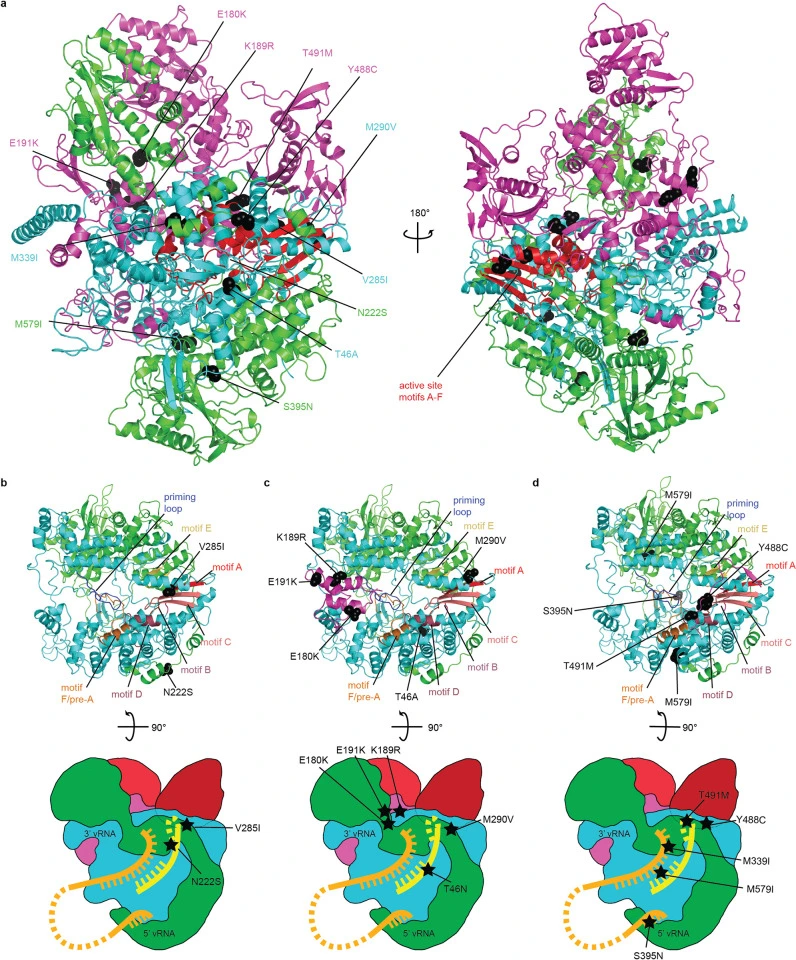
Influenza A virus resistance to 4′-fluorouridine coincides with viral attenuation in vitro and in vivo
Pre-existing or rapidly emerging resistance of influenza viruses to approved antivirals makes the development of novel therapeutics to mitigate seasonal influenza and improve preparedness against future influenza pandemics an urgent priority. We have recently identified the chain-terminating broad-spectrum nucleoside analog clinical candidate 4′-fluorouridine (4′-FlU) and demonstrated oral efficacy against seasonal, pandemic, and highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses in the mouse and ferret model. Here, we have resistance-profiled 4′-FlU against a pandemic A/CA/07/2009 (H1N1) (CA09).
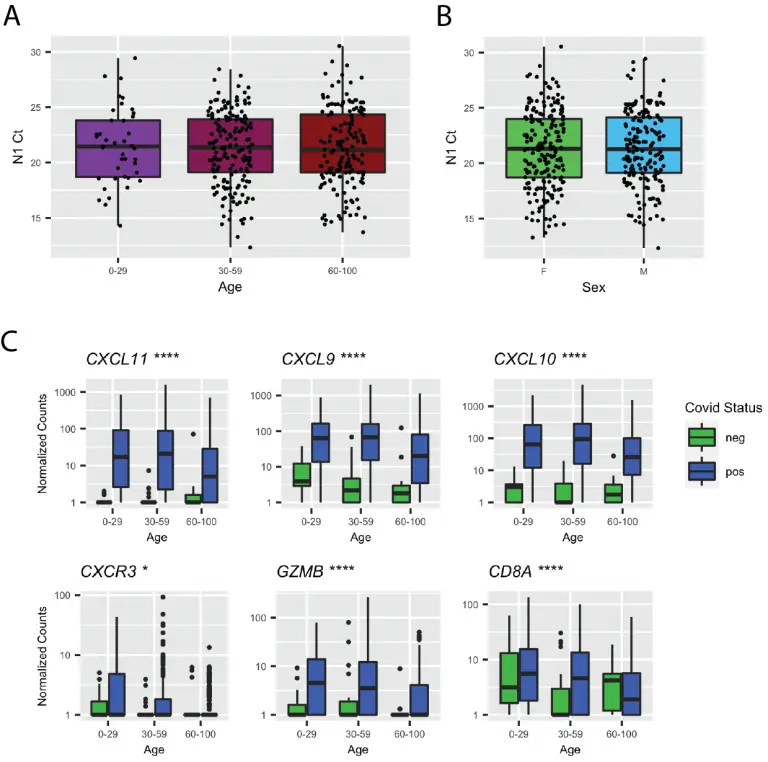
In vivo antiviral host transcriptional response to SARS-CoV-2 by viral load, sex, and age
Despite limited genomic diversity, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has shown a wide range of clinical manifestations in different patient populations. The mechanisms behind these host differences are still unclear. Here, we examined host response gene expression across infection status, viral load, age, and sex among shotgun RNA sequencing profiles of nasopharyngeal (NP) swabs from 430 individuals with PCR-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 and 54 negative controls. SARS-CoV-2 induced a strong antiviral response with up-regulation of antiviral factors such as OAS1-3 and IFIT1-3 and T helper type 1 (Th1) chemokines CXCL9/10/11, as well as a reduction in transcription of ribosomal proteins.
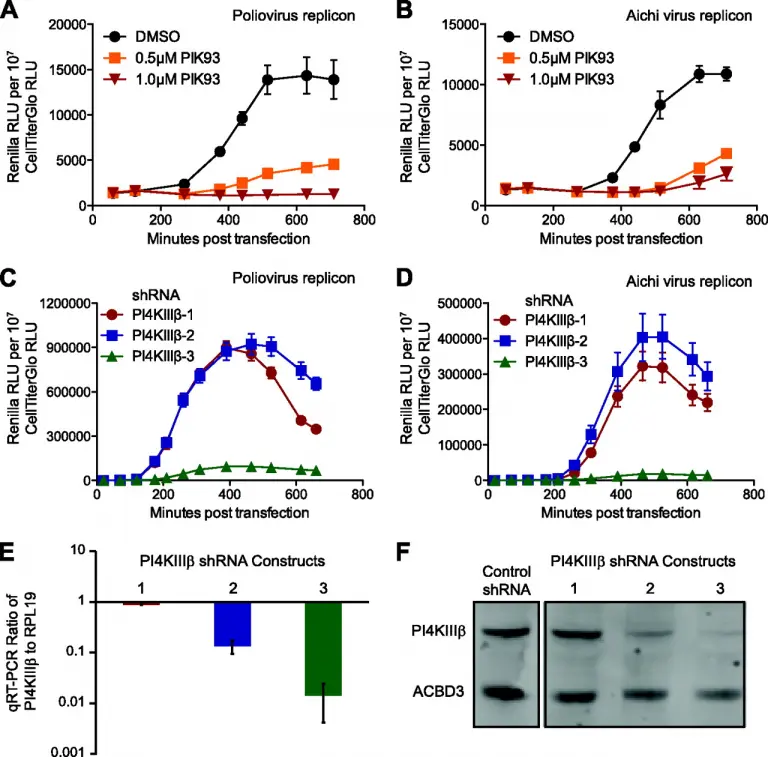
The 3A Protein from Multiple Picornaviruses Utilizes the Golgi Adaptor Protein ACBD3 to Recruit PI4KIIIB
The activity of phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase class III beta (PI4KIIIβ) has been shown to be required for the replication of multiple picornaviruses; however, it is unclear whether a physical association between PI4KIIIβ and the viral replication machinery exists and, if it does, whether association is necessary. We examined the ability of the 3A protein from 18 different picornaviruses to form a complex with PI4KIIIβ by affinity purification of Strep-Tagged transiently transfected constructs followed by mass spectrometry and Western blotting for putative interacting targets.
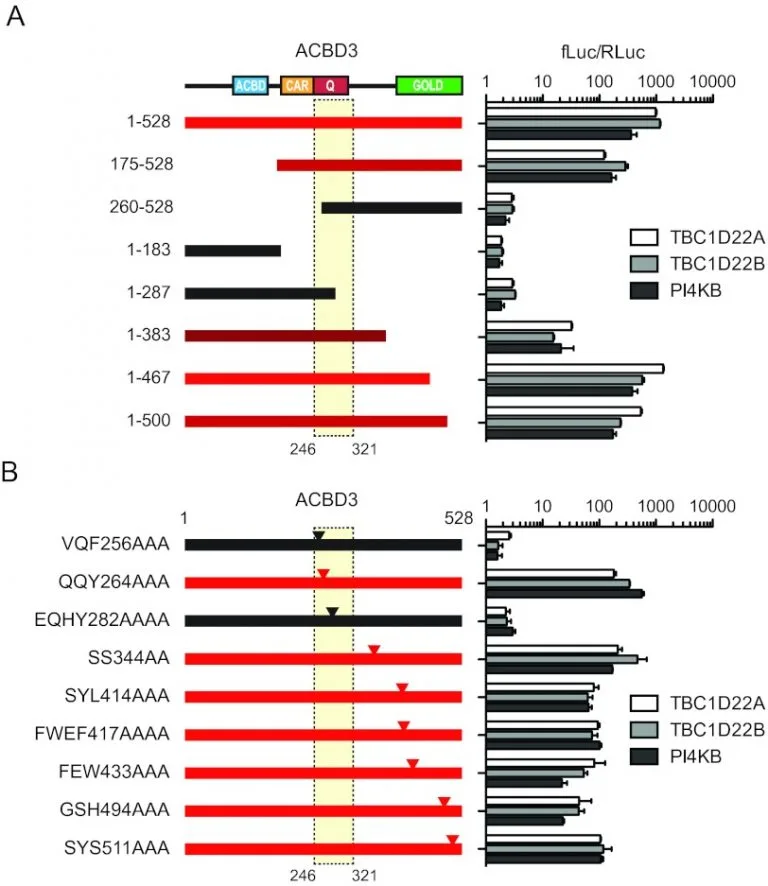
ACBD3 Interaction with TBC1 domain 22 protein is differentially affected by enteroviral and kobuviral 3A protein binding.
Despite wide sequence divergence, multiple picornaviruses use the Golgi adaptor acyl coenzyme A (acyl-CoA) binding domain protein 3 (ACBD3/GCP60) to recruit phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase class III beta (PI4KIIIβ/PI4KB), a factor required for viral replication. The molecular basis of this convergent interaction and the cellular function of ACBD3 are not fully understood. Using affinity purification-mass spectrometry, we identified the putative Rab33 GTPase-activating proteins TBC1D22A and TBC1D22B as ACBD3-interacting factors.
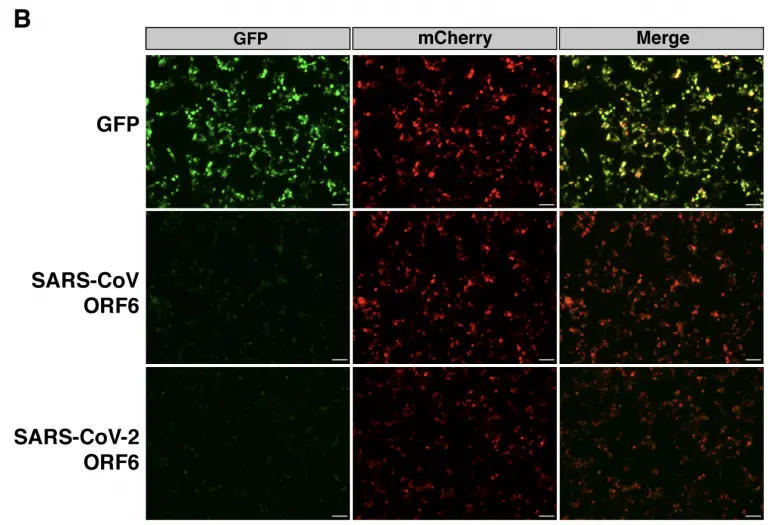
SARS-CoV-2 ORF6 disrupts nucleocytoplasmic transport through interactions with Rae1 and Nup98
RNA viruses that replicate in the cytoplasm often disrupt nucleocytoplasmic transport to preferentially translate their own transcripts and prevent host antiviral responses. The Sarbecovirus accessory protein ORF6 has previously been shown to be a major inhibitor of interferon production in both severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Here, we show SARS-CoV-2-infected cells display an elevated level of nuclear mRNA accumulation compared to mock-infected cells.
CLINICAL VIROLOGY AND MICROBIOLOGY
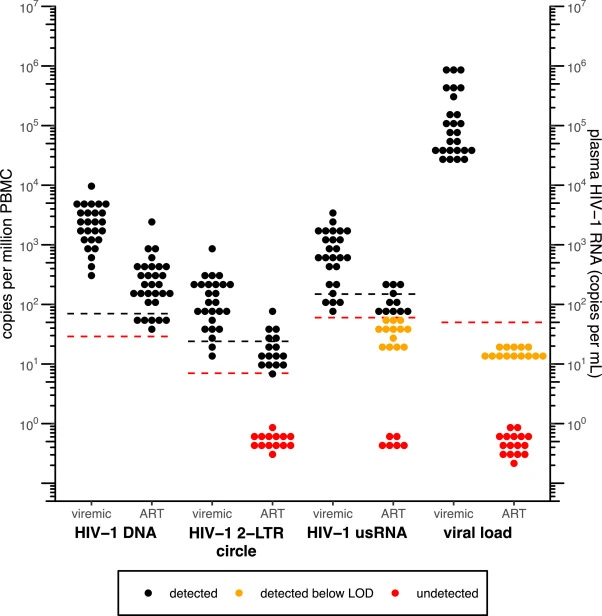
Validation of digital droplet PCR assays for cell-associated HIV-1 DNA, HIV-1 2-LTR circle, and HIV-1 unspliced RNA for clinical studies in HIV-1 cure research
Cell-associated HIV-1 DNA, HIV-1 2-LTR circle, and HIV-1 unspliced RNA (usRNA) are important virological parameters for monitoring HIV-1 persistence and activation of latent HIV-1. Assays fully validated by CLIA and/or GCLP standards are needed for future clinical trials that seek to evaluate treatments directed towards HIV-1 cure.
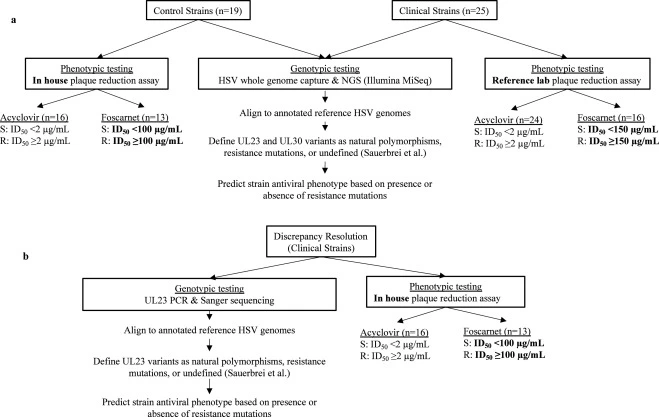
Genotypic testing improves detection of antiviral resistance in human herpes simplex virus
Antiviral resistance in human herpes simplex viruses (HSV) remains a significant clinical challenge in immunocompromised populations. Although molecular tests have largely replaced viral culture for HSV diagnosis and molecular antiviral resistance testing is available for many viruses, HSV resistance testing continues to rely on phenotypic, viral culture-based methods, requiring weeks for results. Consequently, treatment of suspected HSV resistance remains largely empiric.
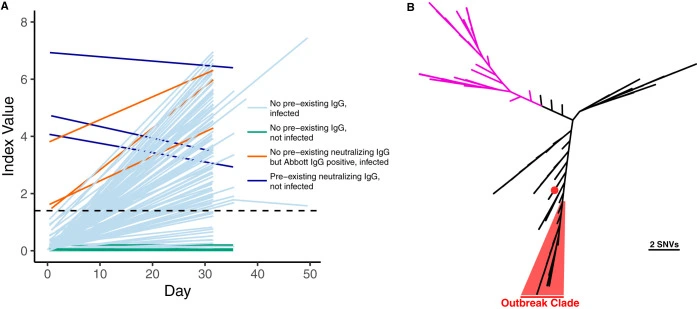
Neutralizing antibodies correlate with protection from SARS-CoV-2 in humans during a fishery vessel outbreak with high attack rate
The development of vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 would be greatly facilitated by the identification of immunological correlates of protection in humans. However, to date, studies on protective immunity have been performed only in animal models and correlates of protection have not been established in humans. Here, we describe an outbreak of SARS-CoV-2 on a fishing vessel associated with a high attack rate.
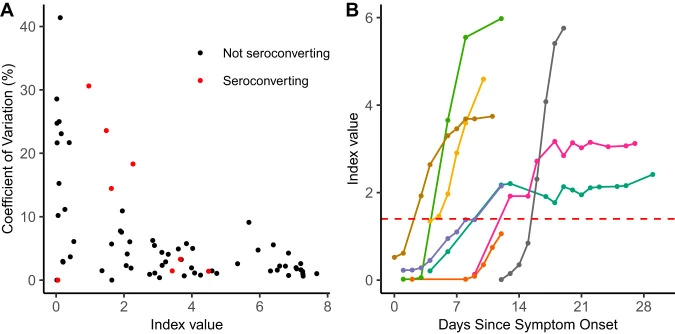
Performance Characteristics of the Abbott Architect SARS-CoV-2 IgG Assay and Seroprevalence in Boise, Idaho
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), the novel respiratory illness caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), is associated with severe morbidity and mortality. The rollout of diagnostic testing in the United States was slow, leading to numerous cases that were not tested for SARS-CoV-2 in February and March 2020 and necessitating the use of serological testing to determine past infections. Here, we evaluated the Abbott SARS-CoV-2 IgG test for detection of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies by testing 3 distinct patient populations.
Evaluation of Genotypic Antiviral Resistance Testing as an Alternative to Phenotypic Testing in a Patient with DOCK8 Deficiency and Severe HSV-1 Disease
Antiviral resistance frequently complicates the treatment of herpes simplex virus (HSV) infections in immunocompromised patients. Here we present the case of an adolescent boy with dedicator of cytokinesis 8 (DOCK8) deficiency, who experienced recurrent infections with resistant HSV-1.
VIRAL GENOMICS, TRANSMISSION, AND DISCOVERY
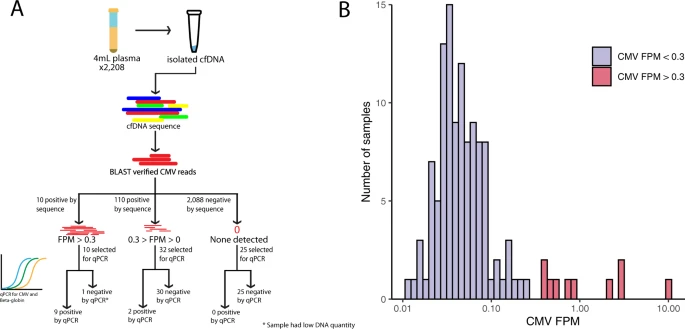
High-resolution profiling of human cytomegalovirus cell-free DNA in human plasma highlights its exceptionally fragmented nature
Human cytomegalovirus (CMV) infections comprise a leading cause of newborn impairments worldwide and are pervasive concerns among the immunocompromised. Quantification of CMV viral loads is increasingly used to guide definitions of CMV disease but standardization of CMV quantitation remains problematic, mostly due to differences in qPCR amplicon sizes between clinical laboratories. Here, we used plasma cfDNA sequencing data from 2,208 samples sent for non-invasive prenatal aneuploidy screening to detect CMV and precisely measure the length of CMV fragments in human plasma.
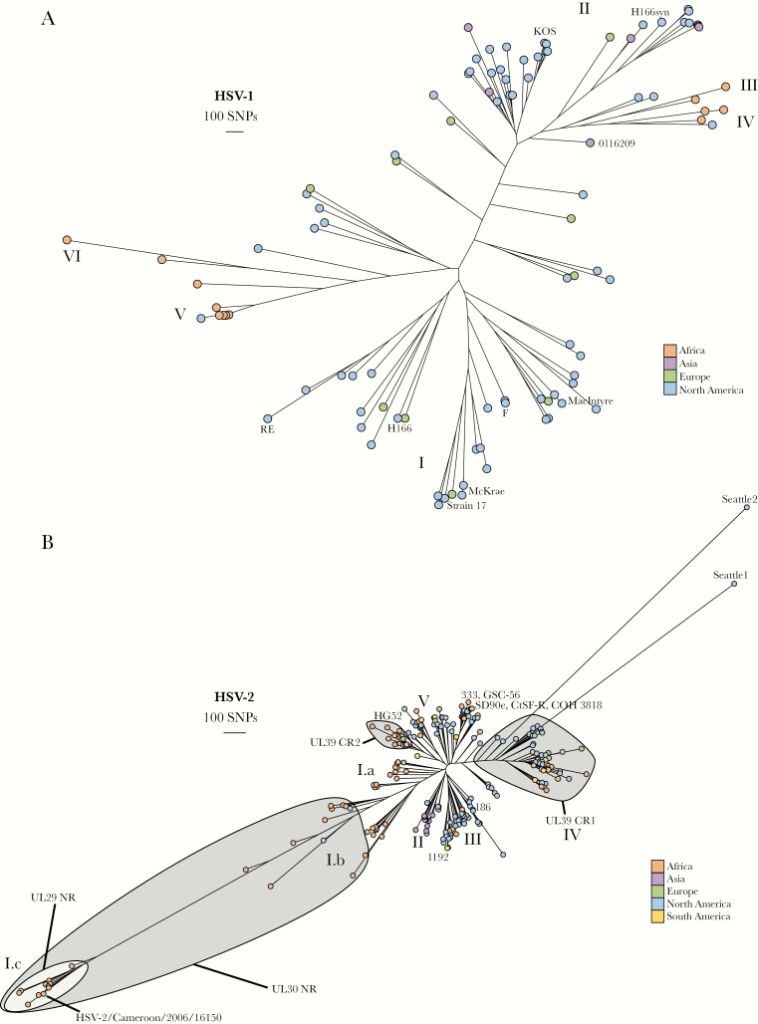
Large, Stable, Contemporary Interspecies Recombination Events in Circulating Human Herpes Simplex Viruses
Human cytomegalovirus (CMV) infections comprise a leading cause of newborn impairments worldwide and are pervasive concerns among the immunocompromised. Quantification of CMV viral loads is increasingly used to guide definitions of CMV disease but standardization of CMV quantitation remains problematic, mostly due to differences in qPCR amplicon sizes between clinical laboratories. Here, we used plasma cfDNA sequencing data from 2,208 samples sent for non-invasive prenatal aneuploidy screening to detect CMV and precisely measure the length of CMV fragments in human plasma. CMV reads were identified in 120 (5.4%) samples. Median cfDNA fragment size derived from CMV was significantly shorter than cfDNA derived from human chromosomes (103 vs 172 bp, p < 0.0001), corresponding to the 3rd percentile of human cfDNA.
BACTERIAL GENOMICS
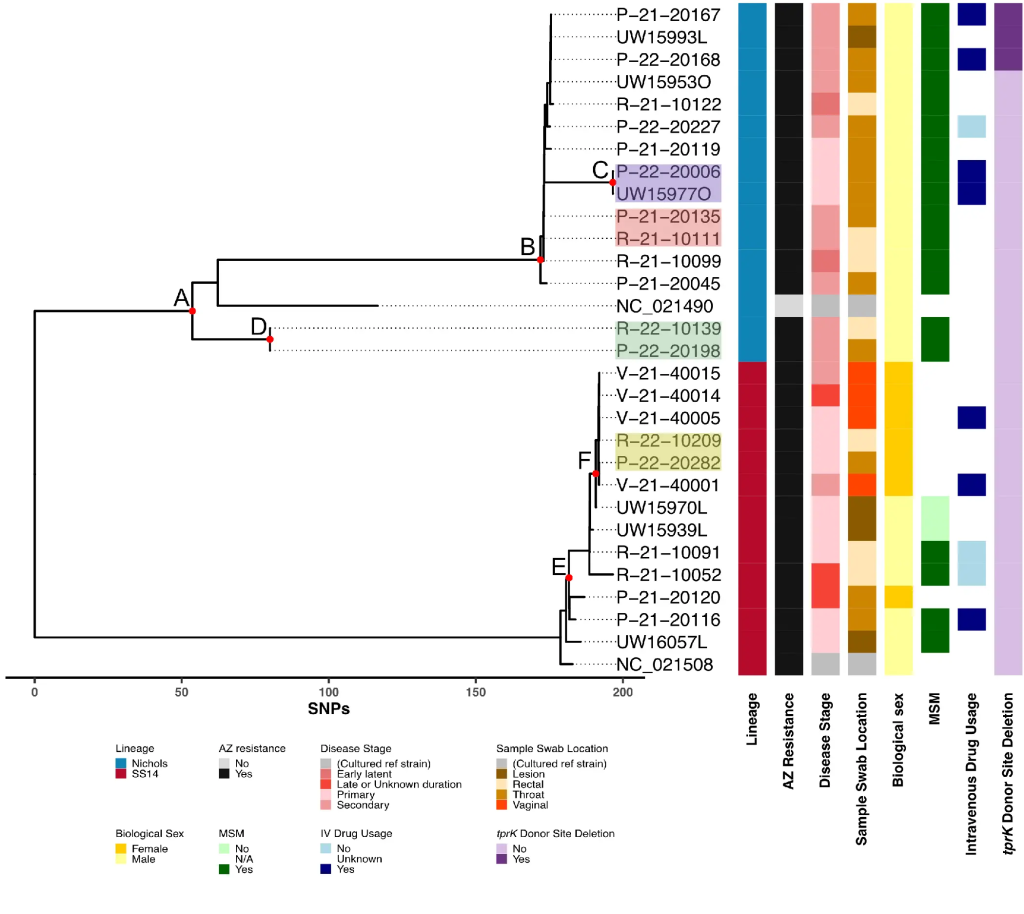
Genomic Epidemiology of Treponema pallidum and Circulation of Strains With Diminished tprK Antigen Variation Capability in Seattle, 2021-2022
We developed an end-to-end workflow for public health genomic surveillance of T. pallidum from remnant Aptima swab specimens. tprK sequencing may assist in linking cases beyond routine T. pallidum genome sequencing. T. pallidum strains with deletions in tprK donor sites currently circulate and are associated with diminished TprK antigenic diversity.
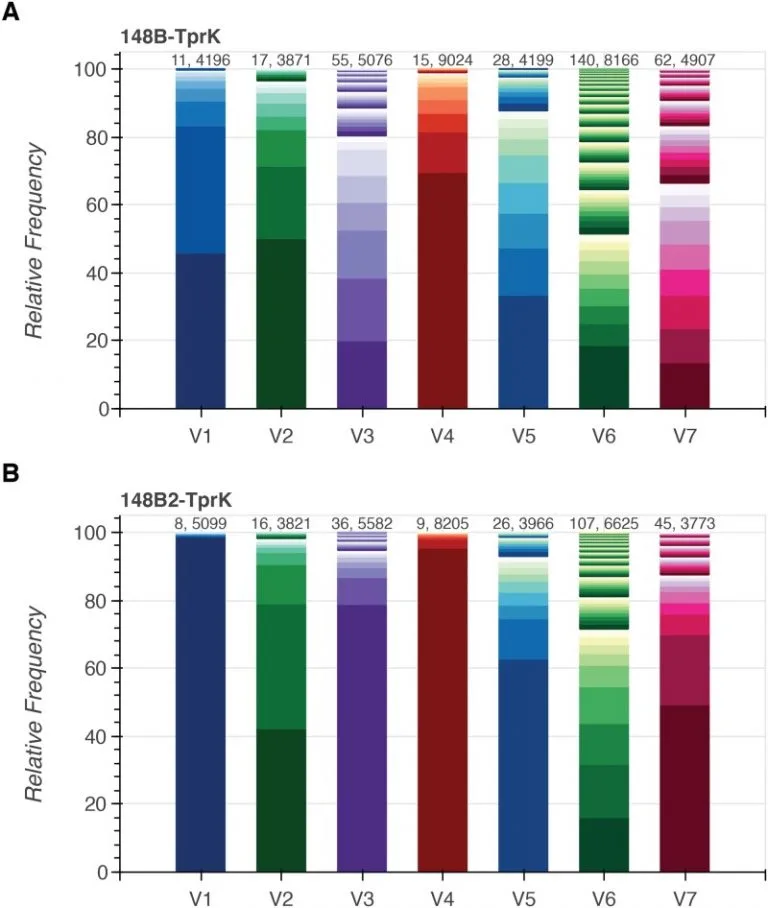
Comparative genomics and full-length Tprk profiling of Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum reinfection
Developing a vaccine against Treponema pallidum subspecies pallidum, the causative agent of syphilis, remains a public health priority. Syphilis vaccine design efforts have been complicated by lack of an in vitro T. pallidum culture system, prolific antigenic variation in outer membrane protein TprK, and lack of functional annotation for nearly half of the genes. Understanding the genetic basis of T. pallidum reinfection can provide insights into variation among strains that escape cross-protective immunity. Here, we present comparative genomic sequencing and deep, full-length tprK profiling of two T. pallidum isolates from blood from the same patient that were collected six years apart.
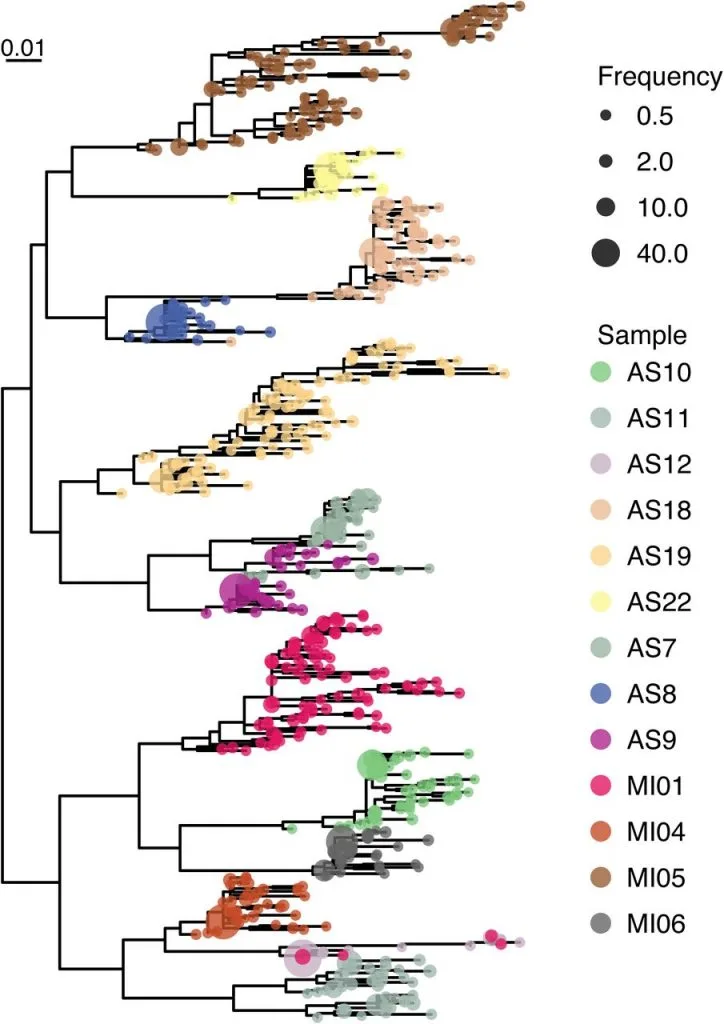
Estimation of Full-Length TprK Diversity in Treponema pallidum subspecies pallidum
Immune evasion and disease progression of Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum are associated with sequence diversity in the hypervariable outer membrane protein TprK. Previous attempts to study variation within TprK have sequenced at depths insufficient to fully appreciate the hypervariable nature of the protein, failed to establish linkage between the protein’s seven variable regions, or were conducted on isolates passed through rabbits. As a consequence, a complete profile of tprK during infection in the human host is still lacking. Furthermore, prior studies examining how T. pallidum subsp. pallidum uses its repertoire of genomic donor sites to generate diversity within the variable regions of the tprK have yielded a partial understanding of this process due to the limited number of tprK alleles examined.
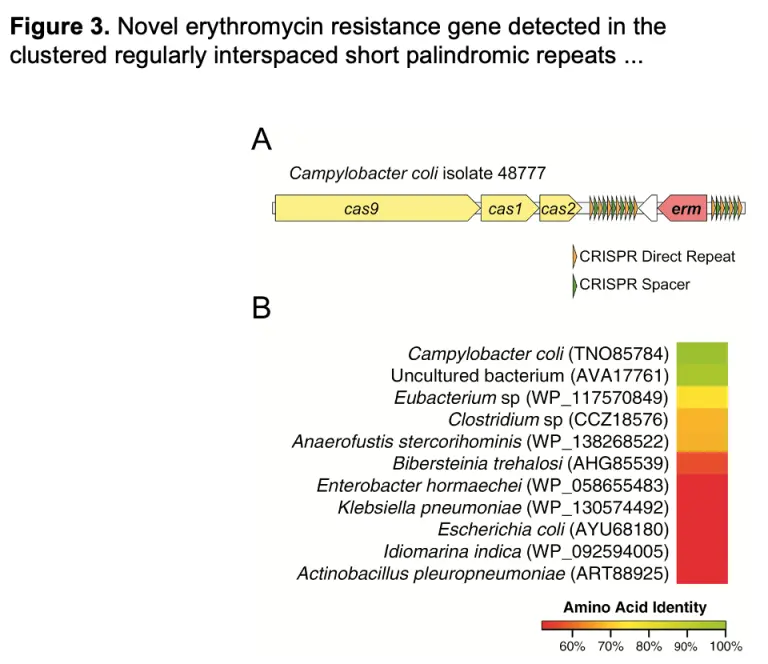
International Spread of Multidrug-Resistant Campylobacter coli in Men who have Sex with Men in Washington State and Quebec, 2015-2018
As previously reported for Shigella, specific multidrug-resistant strains of Campylobacter are circulating by sexual transmission in MSM populations across diverse geographic locations, suggesting a need to incorporate sexual behavior in the investigation of clusters of foodborne pathogens revealed by WGS data.
REVIEWS AND COMMENTARY
The challenge of diagnostic metagenomics
Diagnostic metagenomics and its associated trail of publications are spreading across the world. Multiple clinical labs in the United States, Europe, and Asia have gone to considerable lengths to optimize and validate a range of protocols for agnostically detecting viral, bacterial, fungal, and eukaryotic parasite nucleic acid across a range of patient specimens to aid in diagnosis for particularly recalcitrant cases. Others see a role for diagnostic metagenomics as a frontline diagnostic to replace other microbiological testing.
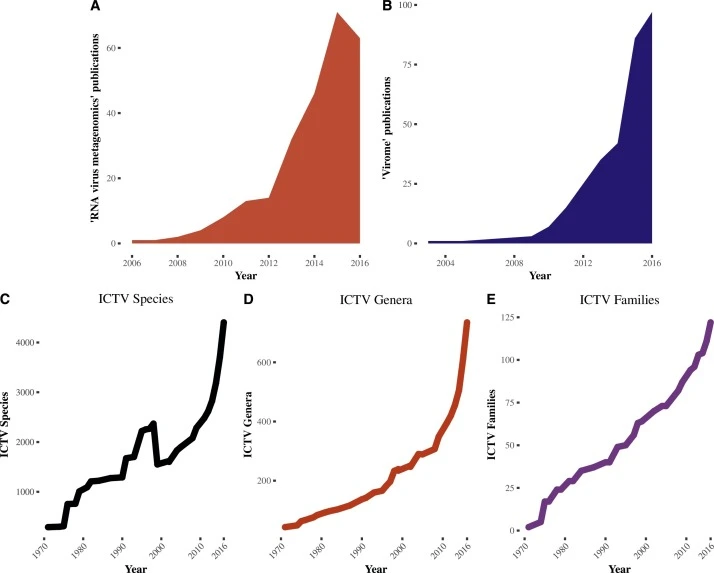
A decade of RNA virus metagenomics is (not) enough
It is hard to overemphasize the role that metagenomics has had on our recent understanding of RNA virus diversity. Metagenomics in the 21st century has brought with it an explosion in the number of RNA virus species, genera, and families far exceeding that following the discovery of the microscope in the 18th century for eukaryotic life or culture media in the 19th century for bacteriology or the 20th century for virology. When the definition of success in organism discovery is measured by sequence diversity and evolutionary distance, RNA viruses win.

Societal Implications of the Internet of Pathogens
The growth of pathogen genomics shows no signs of abating. Whole-genome sequencing of clinical viral and bacterial isolates continues to grow in nearly exponential bounds. Reductions in cost driven by new technology have created a seamless environment for generating, sharing, and analyzing pathogen genomes. The high-resolution view of infectious disease transmission dynamics offered by analyzing whole genomes from pathogens, coupled with the genomicist ethic of widespread data sharing, has created a veritable Internet of pathogens, which inadvertently produces new threats to patient privacy and protected heath information.

The First Quarter of SARS-CoV-2 Testing: the University of Washington Medicine Experience
In early March 2020, the University of Washington Medical Center clinical virology laboratory became one of the first clinical laboratories to offer testing for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). When we first began test development in mid-January, neither of us believed there would be more than 2 million confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infections nationwide or that we would have performed more than 150,000 real-time PCR (RT-PCR) tests, with many more to come.