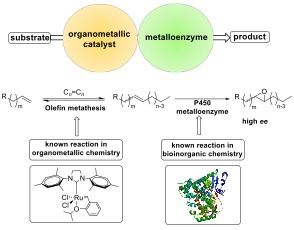
The ability to combine organometallic systems and metalloenzymes would expand the scope of reaction chemistry. However, few conditions have been previously developed that allow for these two complementary types of metal catalysts to react in one-pot. Our research in this area aims to combine the reactivity of a transition metal catalyst with the selectivity engendered by the secondary coordination sphere of a protein to achieve levels of chemo-, regio- and stereoselectivity that are unattainable with a one or multiple small molecule catalysts alone.
We have developed a cooperative catalyst system for the selective transformation of terminal alkenes to internal epoxides.¹ In this reaction, a ruthenium alkene metathesis catalyst creates a dynamic equilibrium among a set of alkenes, and a P450 metalloenzyme selectively epoxides one of these alkenes. The use of these two catalysts in tandem drives the equilibrium mixture of alkenes towards to desired cross metathesis product and enables higher yields than could be obtained by performing each reaction sequentially. Research into the use of additional metalloenzyme/organometallic catalyst combinations is ongoing and aims to provide valuable catalytic transformations under benign reaction conditions.
Reference ¹: Denard, C. A.; Huang, H.; Bartlett, M. J.; Lu, L.; Tan, Y.; Zhao, H.; Hartwig, J. F. "Cooperative Tandem Catalysis by an Organometallic Complex and a Metalloenzyme", Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Eng., 2014, 53, 465-469.
Recent Publications and Patents
© 2007 - 2026 Center for Enabling New Technologies Through Catalysis
centcweb@u.washington.edu
This work was supported by NSF under the CCI Center for Enabling New Technologies Through Catalysis, CHE-1205189. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed here are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation (NSF).