|
|
| C E S S O F T W A R E G U I D E
|
|||||
|
|
|
Introduction to Using CES Architecture and Database | Find Data | Create Charts | Selection | Saving Information Architecture and Database The CES system is a linked set of modules, as shown below. The selection is design-led, meaning that the inputs are the design requirements. These are translated into a prescription for selecting material and process properties.
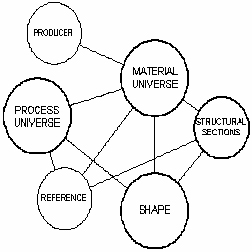
CES Selector is the central module of the CES system. It enables engineers to select, from relational databases, a small subset of entities which optimally satisfy the requirements of a design. The selections may be performed using the CES materials, manufacturing processes or structural sections data modules. Alternatively they may be performed on user-databases developed with CES Constructor. In CES, a database consists of one or more tables (datasets) which are linked together. The core CES database has six linked tables, as shown below. The main selection tables contain materials and manufacturing processes. The supporting tables contain information about producers and references (the sources of information that were used to compile the main tables).
Each
circle represents a table. The lines joining tables
represent links. The two main data tables are organized in the following structure shown in the following flow charts:
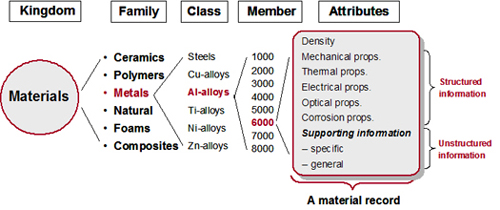
Above is the structure of the Material Universe database.
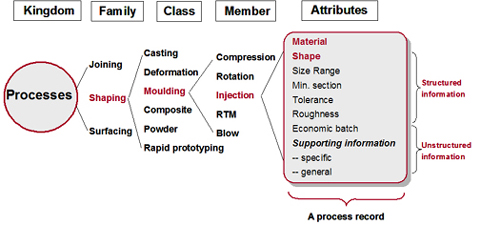
Above is the structure of the Process Universe. |
||
| Copyright © 2006 CES
Information Guide - Materials Science Engineering |
|||||