[Skill Modules
>>
Heart Sounds & Murmurs
>>
Techniques
]
Techniques: Heart Sounds & Murmurs
Murmurs (general) | Systolic | Diastolic
Murmurs
Cardiac murmurs can be divided into three categories based on where they occur in the cardiac cycle.
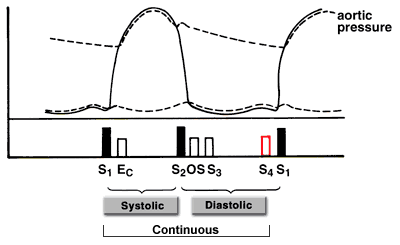
Note: Short, quiet systolic murmurs are generally benign. Long systolic murmurs, diastolic murmurs and continuous murmurs are generally pathologic. (Two continuous murmurs that
are benign are mammary soufflé and cervical venous hum.)
back to top
Intensity of Murmur
| Grade 1 |
just audible with a good stethoscope in a quiet room |
| Grade 2 |
quiet but readily audible with a stethoscope |
| Grade 3 |
easily heard with a stethoscope |
| Grade 4 |
a loud, obvious murmur with a palpable thrill |
| Grade 5 |
very loud, heard only over the pericardium but elsewhere in the body |
| Grade 6 |
heard with stethoscope off chest |
|
