|
|
[Skill Modules
>>
Heart Sounds & Murmurs
>>
Physical Exam
]
Physical Exam: Heart Sounds and & Murmurs
- Peripheral edema
- Jugular venous distension (see JVP below)
- Pulmonary crackles (suspect CHF)
- Cardiac S3
- Positive hepatojugular reflux
|
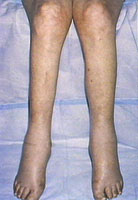
Pitting edema: click for larger image |
Associated signs:
- Water hammer pulse
Due to the large stroke volume and "aortic runoff" of blood from
the aorta back into the left ventricle, there is a sudden rise and abrupt
collapse of peripheral arterial pulse. The term water - hammer pulse comes
from the similar sensation of a water- hammer, a Victorian toy.
To detect this, the radial pulse of a supine patient with arm at side is firmly
palpated with slight pressure until the pulse is obscured. The arm is then
raised over the patient's head, with the arm perpendicular to the supine patient.
Increased pulse pressure
Refers to the difference between the systolic pressure and the diastolic pressure.
Normal is defined as 50-60. A pulse pressure greater than 80 mmHg has a likelihood
ratio of 10.9 A pulse pressure less than 60 has a LR of 0.2.
-
Pistol shot femoral pulse
Refers to short, loud, snapping sounds with each pulse with auscultation over
the femoral, brachial, or radial pulse.
-
Peripheral pulsation
Quincke's: pulsating capillary refill in slightly
compressed fingernail bed
deMusset's sign: bobbing of head with each
heart beat
Lighthouse sign: fluctuating forehead flushing
- When elevated, suspect right-sided heart failure.
- If high JVP, also examine jugular waveforms further for constrictive pericarditis and check pulsus paradox.
|

